Effect of respiratory training on swallowing function in swallowing disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37843618
- PMCID: PMC10858149
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-023-08280-7
Effect of respiratory training on swallowing function in swallowing disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the clinical efficacy of different respiratory training interventions on swallowing function in patients with swallowing disorders through the systematic review.
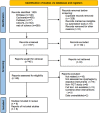
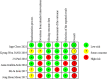
Methods: We reviewed the literature regarding the application of respiratory training therapy in patients with swallowing disorders, followed by a PRISMA search of published literature in five databases (PubMed, Web of Science, The Cochrane Library, CINAHL and EMBASE) in December 2022. Two reviewers performed study selection, quality evaluation, and risk of bias, followed by data extraction and detailed analysis.
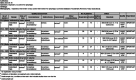
Results: A total of six randomized controlled studies with a total sample size of 193 cases were included. Respiratory training improved swallowing safety (PAS (n = 151, SMD = 0.69, 95% CI - 1.11 to - 0.26, I2 = 36, p < 0.001)) and swallowing efficiency [residual (n = 63, SMD = 1.67, 95% CI - 2.26 to - 1.09, I2 = 23%, p < 0.001)] compared to control groups. The results of the qualitative analysis conducted in this study revealed that respiratory training enhanced hyoid bone movement but had no effect on swallowing quality of life.
Conclusions: Respiratory training interventions may improve swallowing safety and efficiency in patients with dysphagia. However, the level of evidence is low, and there is a limited amount of research on the effectiveness and physiology of this intervention to improve swallowing function. In the future, there is a need to expand clinical studies, standardize measurement tools, and improve study protocols.
Keywords: Breathing exercises; Deglutition disorders; Meta-analysis; Rehabilitation; Respiratory muscles.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no commercial or financial conflict of interests.
Figures


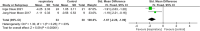
Similar articles
-
Pharyngeal Cavity Electrical Stimulation-Assisted Swallowing for Post-stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies.Dysphagia. 2024 Aug;39(4):541-551. doi: 10.1007/s00455-023-10644-4. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Dysphagia. 2024. PMID: 38117313 Review.
-
Respiratory Muscle Training Reduces Respiratory Complications and Improves Swallowing Function After Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2022 Jun;103(6):1179-1191. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.10.020. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 34780729 Review.
-
Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation associated with swallowing-related muscle training for post-stroke dysphagia: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 19;100(11):e25108. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025108. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33725989 Free PMC article.
-
Swallowing therapy for dysphagia in acute and subacute stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 30;10(10):CD000323. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000323.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30376602 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic exercises for affecting post-treatment swallowing in people treated for advanced-stage head and neck cancers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 26;2016(8):CD011112. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011112.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27562477 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Home-Based Daily Respiratory Muscle Training on Swallowing Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Stroke: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 19;13(18):5547. doi: 10.3390/jcm13185547. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39337034 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative geniohyoid muscle mass in esophageal cancer patients is associated with swallowing function after esophagectomy.Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2024 Jun 26;8(6):1026-1035. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12839. eCollection 2024 Nov. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2024. PMID: 39502723 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Modified Diet, Swallowing Exercises, and Electrostimulation on Quality of Life of Older Patients Suffering from Oropharyngeal Dysphagia.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jun 21;60(7):1021. doi: 10.3390/medicina60071021. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39064450 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

