Pathological and physiological functional cross-talks of α-synuclein and tau in the central nervous system
- PMID: 37843221
- PMCID: PMC10664117
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.382231
Pathological and physiological functional cross-talks of α-synuclein and tau in the central nervous system
Abstract
α-Synuclein and tau are abundant multifunctional brain proteins that are mainly expressed in the presynaptic and axonal compartments of neurons, respectively. Previous works have revealed that intracellular deposition of α-synuclein and/or tau causes many neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Despite intense investigation, the normal physiological functions and roles of α-synuclein and tau are still unclear, owing to the fact that mice with knockout of either of these proteins do not present apparent phenotypes. Interestingly, the co-occurrence of α-synuclein and tau aggregates was found in post-mortem brains with synucleinopathies and tauopathies, some of which share similarities in clinical manifestations. Furthermore, the direct interaction of α-synuclein with tau is considered to promote the fibrillization of each of the proteins in vitro and in vivo. On the other hand, our recent findings have revealed that α-synuclein and tau are cooperatively involved in brain development in a stage-dependent manner. These findings indicate strong cross-talk between the two proteins in physiology and pathology. In this review, we provide a summary of the recent findings on the functional roles of α-synuclein and tau in the physiological conditions and pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. A deep understanding of the interplay between α-synuclein and tau in physiological and pathological conditions might provide novel targets for clinical diagnosis and therapeutic strategies to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: alpha-synuclein; microtubule-associated protein; neurodegenerative disease; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
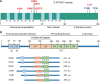
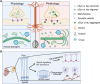
Similar articles
-
O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor ASN90 is a Multimodal Drug Candidate for Tau and α-Synuclein Proteinopathies.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022 Apr 20;13(8):1296-1314. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00057. Epub 2022 Mar 31. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35357812 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of α-synuclein and Tau: A molecular conspiracy in neurodegeneration?Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Mar;99:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 May 10. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 29738880 Review.
-
Alpha-synuclein and tau: teammates in neurodegeneration?Mol Neurodegener. 2014 Oct 29;9:43. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-43. Mol Neurodegener. 2014. PMID: 25352339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mixed pathologies in pancreatic β cells from subjects with neurodegenerative diseases and their interaction with prion protein.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Apr 8;9(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01171-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 33832546 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Cooperation of α-Synuclein and Tau Is Essential for Proper Corticogenesis.J Neurosci. 2022 Sep 14;42(37):7031-7046. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0396-22.2022. Epub 2022 Jul 29. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35906071 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protein modification in neurodegenerative diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 4;5(8):e674. doi: 10.1002/mco2.674. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39105197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fermented Gastrodia elata Bl. Alleviates Cognitive Deficits by Regulating Neurotransmitters and Gut Microbiota in D-Gal/AlCl3-Induced Alzheimer's Disease-like Mice.Foods. 2024 Jul 8;13(13):2154. doi: 10.3390/foods13132154. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38998659 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Intrinsic Disorder in Human Synucleins and Associated Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8399. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158399. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125972 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-synuclein expression in oxytocin neurons of young and old bovine brains.J Reprod Dev. 2024 Aug 7;70(4):213-222. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2024-020. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Reprod Dev. 2024. PMID: 38684411 Free PMC article.
-
Tau Protein Alterations Induced by Hypobaric Hypoxia Exposure.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 10;25(2):889. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020889. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255962 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alim MA, Ma QL, Takeda K, Aizawa T, Matsubara M, Nakamura M, Asada A, Saito T, Kaji H, Yoshii M, Hisanaga S, Uéda K. Demonstration of a role for alpha-synuclein as a functional microtubule-associated protein. J Alzheimers Dis. 2004;6:435–449. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, de Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, Diep L, Keim PS, Shen X, Chataway T, Schlossmacher MG, Seubert P, Schenk D, Sinha S, Gai WP, Chilcote TJ. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:29739–29752. - PubMed
-
- Arima K, Mizutani T, Alim MA, Tonozuka-Uehara H, Izumiyama Y, Hirai S, Uéda K. NACP/alpha-synuclein and tau constitute two distinctive subsets of filaments in the same neuronal inclusions in brains from a family of parkinsonism and dementia with Lewy bodies: double-immunolabeling fluorescence and electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 2000;100:115–121. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

