CRISPR-Cas9 delivery strategies with engineered extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 37842166
- PMCID: PMC10571031
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102040
CRISPR-Cas9 delivery strategies with engineered extracellular vesicles
Abstract
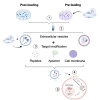
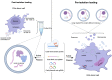
Therapeutic genome editing has the potential to cure diseases by directly correcting genetic mutations in tissues and cells. Recent progress in the CRISPR-Cas9 systems has led to breakthroughs in gene editing tools because of its high orthogonality, versatility, and efficiency. However, its safe and effective administration to target organs in patients is a major hurdle. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are endogenous membranous particles secreted spontaneously by all cells. They are key actors in cell-to-cell communication, allowing the exchange of select molecules such as proteins, lipids, and RNAs to induce functional changes in the recipient cells. Recently, EVs have displayed their potential for trafficking the CRISPR-Cas9 system during or after their formation. In this review, we highlight recent developments in EV loading, surface functionalization, and strategies for increasing the efficiency of delivering CRISPR-Cas9 to tissues, organs, and cells for eventual use in gene therapies.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; MT: Exploiting Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Agents Special Issue; delivery; extracellular vesicles; gene therapy; tissue targeting.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the manuscript was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engineered Cas9 extracellular vesicles as a novel gene editing tool.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 May;11(5):e12225. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12225. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022. PMID: 35585651 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulating Cas9 into extracellular vesicles by protein myristoylation.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 Apr;11(4):e12196. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12196. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022. PMID: 35384352 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-derived extracellular vesicles for CRISPR/Cas9 delivery: engineering strategies for cargo packaging and loading.Biomater Sci. 2022 Jul 26;10(15):4095-4106. doi: 10.1039/d2bm00480a. Biomater Sci. 2022. PMID: 35766814 Review.
-
Exosomes as Targeted Delivery Platform of CRISPR/Cas9 for Therapeutic Genome Editing.Chembiochem. 2021 Dec 10;22(24):3360-3368. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100359. Epub 2021 Sep 12. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 34418266 Review.
-
Engineering extracellular vesicles to deliver CRISPR ribonucleoprotein for gene editing.J Extracell Vesicles. 2023 Sep;12(9):e12343. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12343. J Extracell Vesicles. 2023. PMID: 37723839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles isolated from curcumin-medium weakened RKO cell proliferation and migration.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):2596-2604. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-98. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988906 Free PMC article.
-
Basic Guide for Approaching Drug Delivery with Extracellular Vesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10401. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910401. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome theranostics: Comparative analysis of P body and exosome proteins and their mutations for clinical applications.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Jul 12;24(4):124. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01404-0. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38995459 Review.
-
On RNA-programmable gene modulation as a versatile set of principles targeting muscular dystrophies.Mol Ther. 2024 Nov 6;32(11):3793-3807. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.08.016. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39169620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: A New Star for Gene Drug Delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Mar 6;19:2241-2264. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S446224. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38465204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

