A novel [89Zr]-anti-PD-1-PET-CT to assess response to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in lung cancer
- PMID: 37841258
- PMCID: PMC10569300
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272570
A novel [89Zr]-anti-PD-1-PET-CT to assess response to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Harnessing the anti-tumor immune system response by targeting the program cell death protein (PD-1) and program cell death ligand protein (PD-L1) axis has been a major breakthrough in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) therapy. Nonetheless, conventional imaging tools cannot accurately assess response in immunotherapy-treated patients. Using a lung cancer syngeneic mouse model responder to immunotherapy, we aimed to demonstrate that [89Zr]-anti-PD-1 immuno-PET is a safe and feasible imaging modality to assess the response to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in NSCLC.
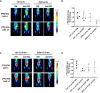
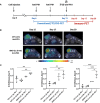
Materials and methods: A syngeneic mouse model responder to anti-PD-1 therapy was used. Tumor growth and response to PD-1 blockade were monitored by conventional 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose ([18F]-FDG) PET scans. Additionally, tumor lymphocyte infiltration was analyzed by the use of an [89Zr]-labeled anti-PD-1 antibody and measured as 89Zr tumor uptake.
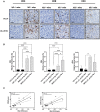
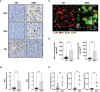
Results: Conventional [18F]-FDG-PET scans failed to detect the antitumor activity exerted by anti-PD-1 therapy. However, [89Zr]-anti-PD-1 uptake was substantially higher in mice that responded to PD-1 blockade. The analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cell populations and interleukins demonstrated an increased anti-tumor effect elicited by activation of effector immune cells in PD-1-responder mice. Interestingly, a positive correlation between [89Zr]-anti-PD-1 uptake and the proportion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) was found (Cor = 0.8; p = 0.001).
Conclusion: Our data may support the clinical implementation of immuno-PET as a promising novel imaging tool to predict and assess the response of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in patients with NSCLC.
Keywords: PD-1 inhibition; immuno-PET; inhibitor of differentiation 1; lung adenocarcinoma; pseudoprogression.
Copyright © 2023 Puyalto, Rodríguez-Remírez, López, Iribarren, Simón, Ecay, Collantes, Vilalta-Lacarra, Francisco-Cruz, Solórzano, Sandiego, Peñuelas, Calvo, Ajona and Gil-Bazo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Predicting the Response to PD-1 Blocking Immunotherapy in Advanced NSCLC Patients with High-Level PD-L1 Expression.Clin Lung Cancer. 2021 Sep;22(5):432-440. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33879398
-
Monitoring the Response of PD-L1 Expression to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer Xenografts by Immuno-PET Imaging.Mol Pharm. 2019 Aug 5;16(8):3469-3476. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00307. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31283253
-
PD-L1 PET/CT Imaging with Radiolabeled Durvalumab in Patients with Advanced-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.J Nucl Med. 2022 May;63(5):686-693. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.262473. Epub 2021 Aug 12. J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 34385342
-
Value of 18F-FDG-PET to predict PD-L1 expression and outcomes of PD-1 inhibition therapy in human cancers.Cancer Imaging. 2021 Jan 13;21(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40644-021-00381-y. Cancer Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33441183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress in Clinical Researches of PD-1/PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibitor for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019 Jul 20;22(7):440-448. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.07.06. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31315783 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Applications of CT-based radiomics for the prediction of immune checkpoint markers and immunotherapeutic outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 22;15:1434171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1434171. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39238640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges coexist with opportunities: development of a macrocyclic peptide PET radioligand for PD-L1.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 May;51(6):1574-1577. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06680-3. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38492018 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rodríguez-Abreu D, Powell SF, Hochmair MJ, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, et al. . Pemetrexed plus platinum with or without pembrolizumab in patients with previously untreated metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC: protocol-specified final analysis from KEYNOTE-189. Ann Oncol (2021) 32:881–95. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.04.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

