The Protective Effect of Roseburia faecis Against Repeated Water Avoidance Stress-induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome in a Wister Rat Model
- PMID: 37830115
- PMCID: PMC10564633
- DOI: 10.15430/JCP.2023.28.3.93
The Protective Effect of Roseburia faecis Against Repeated Water Avoidance Stress-induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome in a Wister Rat Model
Erratum in
-
Erratum: The Protective Effect of Roseburia faecis Against Repeated Water Avoidance Stress-induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome in a Wister Rat Model.J Cancer Prev. 2023 Dec 30;28(4):219. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2023.28.4.219. J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 38205366 Free PMC article.
Abstract
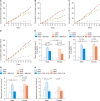
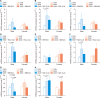
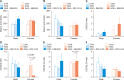
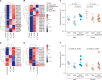
Roseburia faecis, a butyrate-producing, gram-positive anaerobic bacterium, was evaluated for its usefulness against repeated water avoidance stress (WAS)-induced irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in a rat model, and the underlying mechanism was explored. We divided the subjects into three groups: one without stress exposure, another subjected to daily 1-hour WAS for 10 days, and a third exposed to the same WAS regimen while also receiving two different R. faecis strains (BBH024 or R22-12-24) via oral gavage for the same 10-day duration. Fecal pellet output (FPO), a toluidine blue assay for mast cell infiltration, and fecal microbiota analyses were conducted using 16S rRNA metagenomic sequencing. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities in metabolism was also conducted. FPO and colonic mucosal mast cell counts were significantly higher in the WAS group than in the control group (male, P = 0.004; female, P = 0.027). The administration of both BBH024 (male, P = 0.015; female, P = 0.022) and R22-12-24 (male, P = 0.003; female, P = 0.040) significantly reduced FPO. Submucosal mast cell infiltration in the colon showed a similar pattern in males. In case of fecal microbiota, the WAS with R. faecis group showed increased abundance of the Roseburia genus compared to WAS alone. Moreover, the expression of a gene encoding a D-methionine transport system substrate-binding protein was significantly elevated in the WAS with R. faecis group compared to that in the WAS (male, P = 0.028; female, P = 0.025) group. These results indicate that R. faecis is a useful probiotic for treating IBS and colonic microinflammation.
Keywords: Irritable bowel syndrome; Probiotics; Rats; Roseburia faecis.
Copyright © 2023 Korean Society of Cancer Prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sex Difference in the Effect of Bifidobacterium longum on Repeated Water Avoidance Stress-induced Gut Dysbiosis in Wistar Rats.J Cancer Prev. 2024 Mar 30;29(1):16-23. doi: 10.15430/JCP.23.042. Epub 2024 Mar 29. J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38567109 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: The Protective Effect of Roseburia faecis Against Repeated Water Avoidance Stress-induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome in a Wister Rat Model.J Cancer Prev. 2023 Dec 30;28(4):219. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2023.28.4.219. J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 38205366 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effect of butyrate-producing Lachnospiraceae on stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Aug;34(8):1368-1376. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14536. Epub 2018 Dec 16. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30402954 Free PMC article.
-
Roseburia spp.: a marker of health?Future Microbiol. 2017 Feb;12:157-170. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0130. Future Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28139139 Review.
-
Effect of acupuncture on the expression of neuropeptides and related inflammatory factors in rats with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Nov 25;48(11):1142-1150. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20221401. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37984912 Chinese, English.
Cited by
-
Sex Difference in the Effect of Bifidobacterium longum on Repeated Water Avoidance Stress-induced Gut Dysbiosis in Wistar Rats.J Cancer Prev. 2024 Mar 30;29(1):16-23. doi: 10.15430/JCP.23.042. Epub 2024 Mar 29. J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38567109 Free PMC article.
-
The mediating role of metabolites between gut microbiome and Hirschsprung disease: a bidirectional two-step Mendelian randomization study.Front Pediatr. 2024 Aug 27;12:1371933. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1371933. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39258147 Free PMC article.
-
An Oral Botanical Supplement Improves Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) and Facial Redness: Results of an Open-Label Clinical Study.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 18;16(18):3149. doi: 10.3390/nu16183149. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339748 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
