Advances in the study of macrophage polarization in inflammatory immune skin diseases
- PMID: 37828492
- PMCID: PMC10568804
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-023-00360-z
Advances in the study of macrophage polarization in inflammatory immune skin diseases
Abstract
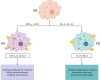
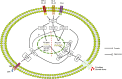
When exposed to various microenvironmental stimuli, macrophages are highly plastic and primarily polarized into the pro-inflammatory M1-type and the anti-inflammatory M2-type, both of which perform almost entirely opposing functions. Due to this characteristic, macrophages perform different functions at different stages of immunity and inflammation. Inflammatory immune skin diseases usually show an imbalance in the M1/M2 macrophage ratio, and altering the macrophage polarization phenotype can either make the symptoms worse or better. Therefore, this review presents the mechanisms of macrophage polarization, inflammation-related signaling pathways (JAK/STAT, NF-κB, and PI3K/Akt), and the role of both in inflammatory immune skin diseases (psoriasis, AD, SLE, BD, etc.) to provide new directions for basic and clinical research of related diseases.
Keywords: Immunity; Inflammation; Macrophage polarization; Signaling pathway; Skin diseases.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophage polarization toward M1 phenotype through NF-κB signaling in patients with Behçet's disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Nov 4;24(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02938-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36333776 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of lipid-induced macrophage polarization through modulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activity affects hepatic lipid metabolism via a Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Nov;35(11):1998-2008. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15025. Epub 2020 Mar 18. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32128893
-
Targeting different phenotypes of macrophages: A potential strategy for natural products to treat inflammatory bone and joint diseases.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154952. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154952. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37506402 Review.
-
Exploring the potential of treating chronic liver disease targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway and polarization mechanism of macrophages.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 9;9(6):e17116. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17116. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37484431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Drive M1 Macrophage Polarization via Exosomal miR-143-3p-Mediated Regulation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Signaling.Stem Cells. 2023 Mar 2;41(2):184-199. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac087. Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 36520505
Cited by
-
The role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immune evasion.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 7;150(5):238. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05777-4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38713256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulatory mechanism of macrophage polarization in diabetic wound healing (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jan;31(1):2. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13367. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39422035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibrous Remodeling in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Clinical Facts and Pathophysiological Uncertainties.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 11;25(2):927. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020927. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of macrophages in rosacea: implications for targeted therapies.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1211953. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1211953. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37691916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cayratia albifolia C.L.Li exerts anti-rheumatoid arthritis effect by inhibiting macrophage activation and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs).Chin Med. 2024 Mar 5;19(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00910-4. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38444022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McComb S, Thiriot A, Akache B, Krishnan L, Stark F. Introduction to the Immune System. Methods in molecular biology. (Clifton NJ) 2019;2024:1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

