Efficacy and safety of finerenone in chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37811017
- PMCID: PMC10553111
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001180
Efficacy and safety of finerenone in chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: The incidence of morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is substantially correlated with cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. The current guidelines recommend the use of renin-angiotensin system blockers, but recent studies probed into the effects of finerenone to mitigate the risk of cardiorenal events. This meta-analysis was performed to demonstrate the effects of finerenone on cardiorenal events, comprising cardiovascular mortality, heart failure, change in estimated glomerular filtration rate, and serum potassium levels.
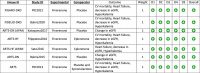
Methods: After screening with our eligibility criteria, 350 articles were identified with an initial literature search on multiple databases, including PubMed, Science Direct, and Cochrane Central. Seven randomized controlled trials with a total of 15 462 patients (n=8487 in the finerenone group; n=6975 in the control group) were included.
Results: Patients receiving finerenone were at a reduced risk for cardiovascular mortality [HR: 0.84 (0.74, 0.95)], heart failure [OR: 0.79 (0.68, 0.92)], decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate by 40% [OR: 0.82 (0.74, 0.91)] and by 57% [OR: 0.70 (0.59, 0.82)]; and a higher incidence of moderate hyperkalemia [OR: 2.25 (1.78, 2.84)].
Conclusion: Finerenone, owing to its better mineralocorticoid affinity, and a much lower risk of adverse effects, promises to be a much better alternative than other renin-angiotensin system blockers available for the treatment of chronic kidney disease patients with type 2 diabetes. Further trials should be conducted to provide more definitive evidence to assess the safety and efficacy of finerenone compared to spironolactone and eplerenone.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease (CKD); finerenone; meta-analysis; mineralocorticoid receptor antagnosits (MRA); type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
I undersign, certificate that I do not have any financial or personal relationships that might bias the content of this work.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
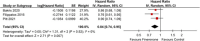






Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: the FIDELITY pooled analysis.Eur Heart J. 2022 Feb 10;43(6):474-484. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab777. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 35023547 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Finerenone in Hispanic Patients With CKD and Type 2 Diabetes: A Post Hoc FIDELITY Analysis.Kidney Med. 2023 Aug 1;5(10):100704. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100704. eCollection 2023 Oct. Kidney Med. 2023. PMID: 37745646 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in patients with diabetic kidney disease.Postgrad Med. 2023 Apr;135(3):224-233. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2060598. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Postgrad Med. 2023. PMID: 35392754 Review.
-
Finerenone: A Third-Generation MRA and Its Impact on Cardiovascular Health-Insights from Randomized Controlled Trials.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 25;13(21):6398. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216398. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone Therapy in Patients with Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cureus. 2023 Jul 11;15(7):e41746. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41746. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37575756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The significance of finerenone as a novel therapeutic option in diabetic kidney disease: a scoping review with emphasis on cardiorenal outcomes of the finerenone phase 3 trials.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 14;11:1384454. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1384454. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38947237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- 11. Microvascular Complications and Foot Care. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43(suppl 1):S135–S151. - PubMed
-
- Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al. . 2019 update to: management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2020;63:221–228. - PubMed
-
- Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, et al. . Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2020;383:2219–2229. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
