p21 promotes gemcitabine tolerance in A549 cells by inhibiting DNA damage and altering the cell cycle
- PMID: 37809050
- PMCID: PMC10551858
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2023.14059
p21 promotes gemcitabine tolerance in A549 cells by inhibiting DNA damage and altering the cell cycle
Abstract
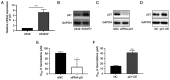
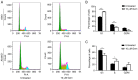
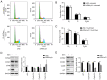
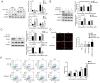
Gemcitabine is one of the most widely used chemotherapy drugs for advanced malignant tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer. However, the clinical efficacy of gemcitabine is limited due to drug resistance. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of p21 in gemcitabine-resistant A549 (A549/G+) lung cancer cells. IC50 values were determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. mRNA and protein expression levels of genes were measured by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and western blotting, respectively. The cell cycle distribution and apoptosis rate were analyzed by flow cytometry. DNA damage in cells was evaluated by single-cell gel electrophoresis. The results of western blot analysis and the CCK-8 assay demonstrated that the expression of p21 was higher in A549/G+ cells than in gemcitabine-sensitive cells. Knockdown of p21 expression in gemcitabine-resistant cells sensitized these cells to gemcitabine (with the IC50 decreasing from 84.2 to 26.7 µM). Cell cycle analysis revealed different changes in the cell cycle distribution in A549/G+ cells treated with the same concentration of gemcitabine, and decreased expression of p21 was shown to promote G1 arrest. The apoptosis assay and comet assay results revealed that decreased p21 expression resulted in accumulation of unrepaired DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and induction of apoptosis by gemcitabine. The present study demonstrated that knockout of p21 mRNA expression in A549/G+ cells promotes apoptosis and DNA DSB accumulation, accompanied by G1 arrest. These results indicated that p21 is involved in regulating the response of A549 cells to gemcitabine.
Keywords: A549 cells; DNA damage; drug resistance; gemcitabine; p21.
Copyright: © Fu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HY253, a novel decahydrofluorene analog, from Aralia continentalis, induces cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase and cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 May 4;129(1):135-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.02.010. Epub 2010 Feb 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20219657
-
Co-inhibition of Pol η and ATR sensitizes cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin by impeding DNA damage repair.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Aug;39(8):1359-1372. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.187. Epub 2018 May 31. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29849128 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0096157 contributes to cisplatin resistance by proliferation, cell cycle progression, and suppressing apoptosis of non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Dec;475(1-2):63-77. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03860-1. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32767026
-
Cell cycle disturbances and apoptosis induced by topotecan and gemcitabine on human lung cancer cell lines.Eur J Cancer. 1999 May;35(5):796-807. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(98)00425-0. Eur J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10505042
-
Gemcitabine inhibits cisplatin resistance in cisplatin-resistant A549 cells by upregulating trx-interacting protein and inducing cell cycle arrest.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Apr 9;524(3):549-554. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.01.130. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32014255
Cited by
-
CIP/KIP and INK4 families as hostages of oncogenic signaling.Cell Div. 2024 Apr 1;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13008-024-00115-z. Cell Div. 2024. PMID: 38561743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
