The USP46 deubiquitylase complex increases Wingless/Wnt signaling strength by stabilizing Arrow/LRP6
- PMID: 37798281
- PMCID: PMC10556106
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41843-0
The USP46 deubiquitylase complex increases Wingless/Wnt signaling strength by stabilizing Arrow/LRP6
Abstract
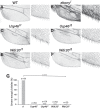
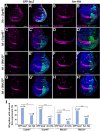
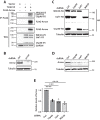
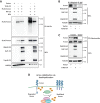
The control of Wnt receptor abundance is critical for animal development and to prevent tumorigenesis, but the mechanisms that mediate receptor stabilization remain uncertain. We demonstrate that stabilization of the essential Wingless/Wnt receptor Arrow/LRP6 by the evolutionarily conserved Usp46-Uaf1-Wdr20 deubiquitylase complex controls signaling strength in Drosophila. By reducing Arrow ubiquitylation and turnover, the Usp46 complex increases cell surface levels of Arrow and enhances the sensitivity of target cells to stimulation by the Wingless morphogen, thereby increasing the amplitude and spatial range of signaling responses. Usp46 inactivation in Wingless-responding cells destabilizes Arrow, reduces cytoplasmic accumulation of the transcriptional coactivator Armadillo/β-catenin, and attenuates or abolishes Wingless target gene activation, which prevents the concentration-dependent regulation of signaling strength. Consequently, Wingless-dependent developmental patterning and tissue homeostasis are disrupted. These results reveal an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that mediates Wnt/Wingless receptor stabilization and underlies the precise activation of signaling throughout the spatial range of the morphogen gradient.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
D.J.R. and E.L. are founders of StemSynergy Therapeutics Inc., a company commercializing small-molecule cell signaling inhibitors, including Wnt inhibitors. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The USP46 complex deubiquitylates LRP6 to promote Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 5;14(1):6173. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41836-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37798301 Free PMC article.
-
Erect Wing facilitates context-dependent Wnt/Wingless signaling by recruiting the cell-specific Armadillo-TCF adaptor Earthbound to chromatin.Development. 2011 Nov;138(22):4955-67. doi: 10.1242/dev.068890. Development. 2011. PMID: 22028028 Free PMC article.
-
Arf6 is necessary for senseless expression in response to wingless signalling during Drosophila wing development.Biol Open. 2021 Dec 1;10(12):bio058892. doi: 10.1242/bio.058892. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Biol Open. 2021. PMID: 34779478 Free PMC article.
-
Wingless Signaling: A Genetic Journey from Morphogenesis to Metastasis.Genetics. 2018 Apr;208(4):1311-1336. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300157. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29618590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/Wingless signaling in Drosophila.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Jun 1;4(6):a007930. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007930. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22535229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wg/Wnt-signaling-induced nuclear translocation of β-catenin is attenuated by a β-catenin peptide through its interference with the IFT-A complex.Cell Rep. 2024 Jun 25;43(6):114362. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114362. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38870008 Free PMC article.
-
The USP46 complex deubiquitylates LRP6 to promote Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 5;14(1):6173. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41836-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37798301 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 GM113132/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG000739/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD018537/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA219189/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM145596/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD032310/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244188/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM137793/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118082/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD010949/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA281002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008554/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM136233/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

