Research progress of the CXCR4 mechanism in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37786419
- PMCID: PMC10528775
- DOI: 10.1002/ibra.12026
Research progress of the CXCR4 mechanism in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
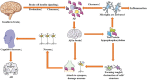
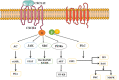
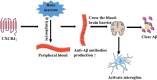
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a degenerative brain disease with complex clinical manifestations and pathogeneses such as abnormal deposition of beta-amyloid protein and inflammation caused by the excessive activation of microglia. CXC motif chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) is a type of G protein-coupled receptor that binds to CXC motif ligand 12 (CXCL12) to activate downstream signaling pathways, such as the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription and the renin-angiotensin system (Ras)/RAF proto-oncogene serine (Raf)/mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular-regulated protein kinase; most of these signaling pathways are involved in inflammatory responses. CXCR4 is highly expressed in the microglia and astrocytes; this might be one of the important causes of inflammation caused by microglia and astrocytes. In this review, we summarize the mechanism and therapeutics of AD, the structures of CXCR4 and the CXCL12 ligand, and the mechanisms of CXCR4/CXCL12 that are involved in the occurrence and development of AD. The possible treatment of AD through microglia and astrocytes is also discussed, with the aim of providing a new method for the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; CXCL12; CXCR4; astrocytes; microglia.
© 2022 The Authors. Ibrain published by Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (AHZMU) and Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CXCL12/CXCR4 chemokine signaling in spinal glia induces pain hypersensitivity through MAPKs-mediated neuroinflammation in bone cancer rats.J Neurochem. 2015 Feb;132(4):452-63. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12985. Epub 2015 Jan 26. J Neurochem. 2015. Retraction in: J Neurochem. 2017 May;141(3):473-474. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13949 PMID: 25393328 Retracted.
-
Chemokine CXCL12 activates dual CXCR4 and CXCR7-mediated signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer cells.J Transl Med. 2012 Apr 2;10:68. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-68. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22472349 Free PMC article.
-
A focus on CXCR4 in Alzheimer's disease.Brain Circ. 2017 Oct-Dec;3(4):199-203. doi: 10.4103/bc.bc_13_17. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Brain Circ. 2017. PMID: 30276325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocytosis is required for CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-mediated Akt activation and antiapoptotic signaling.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 20;293(29):11470-11480. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001872. Epub 2018 Jun 13. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29899118 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Japanese encephalitis virus: Neuroinflammation and neuronal cell damage.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):968-980. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1899674. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33724154 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A meta-analysis of bulk RNA-seq datasets identifies potential biomarkers and repurposable therapeutics against Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 21;14(1):24717. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75431-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39433822 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analysis of Cortex Single-Cell Transcriptome and Serum Proteome Reveals the Novel Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease.Brain Sci. 2022 Aug 1;12(8):1022. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12081022. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36009085 Free PMC article.
-
Common molecular signatures between coronavirus infection and Alzheimer's disease reveal targets for drug development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 15:2023.06.14.544970. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.14.544970. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;95(3):995-1011. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230684 PMID: 37398415 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Understanding global changes of the mouse brain proteome after vaginal infection with HSV-2 using a label-free shotgun approach.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 18;12:942334. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.942334. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36061859 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of microarray datasets to identify biological regulatory networks in Alzheimer's disease.Front Genet. 2023 Aug 29;14:1225196. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1225196. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37705610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer's Association Report . 2020 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures; March 2020. 10.1002/alz.12068 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
