Metabolite Neu5Ac triggers SLC3A2 degradation promoting vascular endothelial ferroptosis and aggravates atherosclerosis progression in ApoE-/-mice
- PMID: 37771765
- PMCID: PMC10526676
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.87968
Metabolite Neu5Ac triggers SLC3A2 degradation promoting vascular endothelial ferroptosis and aggravates atherosclerosis progression in ApoE-/-mice
Abstract
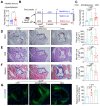
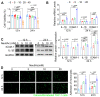
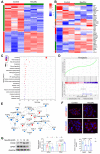
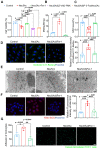
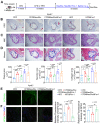
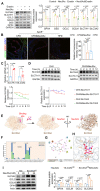
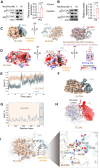
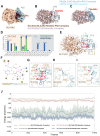
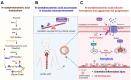
Background: Atherosclerosis (AS) is still the major cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD) as well as stroke. Endothelial metabolic disorder has been found to be activated and then promote endothelial cells (ECs) injury, which is regarded to initiate AS progression. N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), a metabolite produced by hexosamine-sialic acid pathway branching from glucose metabolism, was presented as a notable biomarker of CVD and is positively correlated with ECs function. However, few studies explain whether Neu5Ac regulate AS progression by affecting EC function as well as its involved mechanisms are still unknown. Methods: Here, we mimicked an animal model in ApoE-/- mice which displaying similar plasma Neu5Ac levels with AS model to investigate its effect on AS progression. Results: We found that Neu5Ac exacerbated plaques area and increased lipids in plasma in absence of HFD feeding, and ECs inflammatory injury was supposed as the triggering factor upon Neu5Ac treatment with increasing expression of IL-1β, ICAM-1, and promoting ability of monocyte adhesion to ECs. Mechanistic studies showed that Neu5Ac facilitated SLC3A2 binding to ubiquitin and then triggered P62 mediated degradation, further leading to accumulation of lipid peroxidation in ECs. Fer-1 could inhibit ECs injury and reverse AS progression induced by Neu5Ac in ApoE-/- mice. Interestingly, mitochondrial dysfunction was also partly participated in ECs injury after Neu5Ac treatment and been reversed by Fer-1. Conclusions: Together, our study unveils a new mechanism by which evaluated metabolite Neu5Ac could promote SLC3A2 associated endothelial ferroptosis to activate ECs injury and AS plaque progression, thus providing a new insight into the role of Neu5Ac-ferroptosis pathway in AS. Also, our research revealed that pharmacological inhibition of ferroptosis may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for premature AS.
Keywords: Neu5Ac, ferroptosis, SLC3A2; atherosclerosis, endothelial inflammatory injury.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-acetylneuraminic acid modulates SQSTM1/p62 sialyation-mediated ubiquitination degradation contributing to vascular endothelium dysfunction in experimental atherosclerosis mice.IUBMB Life. 2024 Mar;76(3):161-178. doi: 10.1002/iub.2788. Epub 2023 Oct 11. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 37818680
-
Gualou-Xiebai herb pair ameliorate atherosclerosis in HFD-induced ApoE-/- mice and inhibit the ox-LDL-induced injury of HUVECs by regulating the Nrf2-mediated ferroptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 May 23;326:117892. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117892. Epub 2024 Feb 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38350505
-
Qixian granule inhibits ferroptosis in vascular endothelial cells by modulating TRPML1 in the lysosome to prevent postmenopausal atherosclerosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jun 28;328:118076. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118076. Epub 2024 Mar 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38521431
-
ROS-triggered endothelial cell death mechanisms: Focus on pyroptosis, parthanatos, and ferroptosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 1;13:1039241. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039241. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 6;34:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35024180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N-Acetylneuraminic acid triggers endothelial pyroptosis and promotes atherosclerosis progression via GLS2-mediated glutaminolysis pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Nov 13;10(1):467. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02233-7. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39537619 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis: a potential target for the treatment of atherosclerosis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Mar 25;56(3):331-344. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024016. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38327187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic noise exposure induces Alzheimer's disease-like neuropathology and cognitive impairment via ferroptosis in rat hippocampus.Environ Health Prev Med. 2024;29:50. doi: 10.1265/ehpm.24-00126. Environ Health Prev Med. 2024. PMID: 39343514 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis-related oxaliplatin resistance in multiple cancers: Potential roles and therapeutic Implications.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 7;10(18):e37613. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37613. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39309838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of m6A-associated ferroptosis-related genes in atherosclerosis based on WGCNA.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Oct 28;11:1469805. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1469805. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39529974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019. 139. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021;592:524–33. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Sun X, Carmeliet P. Hallmarks of Endothelial Cell Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2019;30:414–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

