Novel Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Transcript AL137782.1 Promotes the Migration of Normal Lung Epithelial Cells through Positively Regulating LMO7
- PMID: 37762205
- PMCID: PMC10530982
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241813904
Novel Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Transcript AL137782.1 Promotes the Migration of Normal Lung Epithelial Cells through Positively Regulating LMO7
Abstract
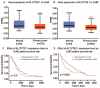
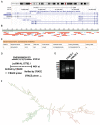
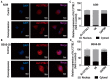
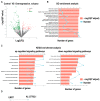
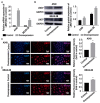
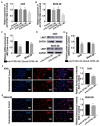
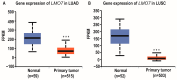
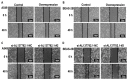
The role of long non-coding RNA (lncRNAs) in biological processes remains poorly understood, despite their significant impact. Our previous research discovered that the expression of AL137782.1, a long transcript of the novel lncRNA ENSG00000261553, is upregulated in lung epithelial cells upon exposure to microbes. Furthermore, the expression of AL137782.1 exhibits variability between para-cancerous and lung adenocarcinoma samples. These findings imply that this lncRNA may play a role in both normal lung epithelial cellular processes and pathophysiology. To elucidate the function of AL137782.1 in lung epithelial cells, we utilized bioinformatics retrieval and analysis to examine its expression. We then analyzed its subcellular localization using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and subcellular fractionation. Through rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE), we confirmed the presence of a 4401 nt lncRNA AL137782.1 in lung epithelial cells. Moreover, we discovered that this lncRNA positively regulates both mRNA and the protein expression of LMO7, a protein that may regulate the cell migration of normal lung epithelial cells. Although the overexpression of AL137782.1 has been shown to enhance the migration of both normal lung epithelial cells and lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro, our study revealed that the expression of this lncRNA was significantly decreased in lung cancers compared to adjacent tissues. This suggests that the cell migration pattern regulated by the AL137782.1-LMO7 axis is more likely to occur in normal lung epithelial cells, rather than being a pathway that promotes lung cancer cell migration. Therefore, our study provides new insights into the mechanism underlying cell migration in human lung epithelial cells. This finding may offer a potential strategy to enhance normal lung epithelial cell migration after lung injury.
Keywords: LMO7; cell migration; lncRNA AL137782.1; lung epithelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA PCAT6 promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cell by targeting miR-545-3p.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3557-3568. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08259-x. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36787056 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MAFG-AS1 Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Targeting miR-3196 and Regulating SOX12 Expression.Mol Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;64(9):970-983. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00455-7. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Mol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35275356
-
LncRNA PKMYT1AR promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating Wnt signaling pathway.Mol Cancer. 2021 Dec 2;20(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01469-6. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34856993 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA FAM83A antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA FAM83A-AS1) targets microRNA-141-3p to regulate lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):4964-4977. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2037871. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35164653 Free PMC article.
-
Role of LMO7 in cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2024 Sep;52(3):117. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8776. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38994754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kawakita N., Toba H., Miyoshi K., Sakamoto S., Matsumoto D., Takashima M., Aoyama M., Inoue S., Morimoto M., Nishino T., et al. Bronchioalveolar stem cells derived from mouse-induced pluripotent stem cells promote airway epithelium regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020;11:430. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01946-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhargava M., Dey S., Becker T., Steinbach M., Wu B., Lee S.M., Higgins L., Kumar V., Bitterman P.B., Ingbar D.H., et al. Protein expression profile of rat type two alveolar epithelial cells during hyperoxic stress and recovery. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013;305:L604–L614. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00079.2013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jansing N.L., McClendon J., Henson P.M., Tuder R.M., Hyde D.M., Zemans R.L. Unbiased Quantitation of Alveolar Type II to Alveolar Type I Cell Transdifferentiation during Repair after Lung Injury in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017;57:519–526. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0037MA. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

