A Supportive Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Insulin-Producing Langerhans Islets with a Specific Emphasis on The Secretome
- PMID: 37761001
- PMCID: PMC10527322
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11092558
A Supportive Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Insulin-Producing Langerhans Islets with a Specific Emphasis on The Secretome
Abstract
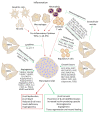
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by a gradual destruction of insulin-producing β-cells in the endocrine pancreas due to innate and specific immune responses, leading to impaired glucose homeostasis. T1D patients usually require regular insulin injections after meals to maintain normal serum glucose levels. In severe cases, pancreas or Langerhans islet transplantation can assist in reaching a sufficient β-mass to normalize glucose homeostasis. The latter procedure is limited because of low donor availability, high islet loss, and immune rejection. There is still a need to develop new technologies to improve islet survival and implantation and to keep the islets functional. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent non-hematopoietic progenitor cells with high plasticity that can support human pancreatic islet function both in vitro and in vivo and islet co-transplantation with MSCs is more effective than islet transplantation alone in attenuating diabetes progression. The beneficial effect of MSCs on islet function is due to a combined effect on angiogenesis, suppression of immune responses, and secretion of growth factors essential for islet survival and function. In this review, various aspects of MSCs related to islet function and diabetes are described.
Keywords: Langerhans’ islets; growth factors; insulin; mesenchymal stem cells; β-cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of marginal mass required for successful islet transplantation in a diabetic rat model using adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.Cytotherapy. 2018 Sep;20(9):1124-1142. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Cytotherapy. 2018. PMID: 30068495
-
Durable Control of Autoimmune Diabetes in Mice Achieved by Intraperitoneal Transplantation of "Neo-Islets," Three-Dimensional Aggregates of Allogeneic Islet and "Mesenchymal Stem Cells".Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Jul;6(7):1631-1643. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0005. Epub 2017 May 3. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28467694 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell secretory molecules improve the functional survival of human islets.Diabet Med. 2023 Dec;40(12):e15227. doi: 10.1111/dme.15227. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Diabet Med. 2023. PMID: 37728506 Free PMC article.
-
Protecting islet functional viability using mesenchymal stromal cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 May;10(5):674-680. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0466. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33544449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem Cell-Based Clinical Trials for Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 26;12:631463. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.631463. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33716982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 May 6;12:1349050. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1349050. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38770273 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

