RNF126, 168 and CUL1: The Potential Utilization of Multi-Functional E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Genome Maintenance for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 37760968
- PMCID: PMC10526535
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11092527
RNF126, 168 and CUL1: The Potential Utilization of Multi-Functional E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Genome Maintenance for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
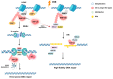
Ubiquitination is a post-translational modification (PTM) that is involved in proteolysis, protein-protein interaction, and signal transduction. Accumulation of mutations and genomic instability are characteristic of cancer cells, and dysfunction of the ubiquitin pathway can contribute to abnormal cell physiology. Because mutations can be critical for cells, DNA damage repair, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis are pathways that are in close communication to maintain genomic integrity. Uncontrolled cell proliferation due to abnormal processes is a hallmark of cancer, and mutations, changes in expression levels, and other alterations of ubiquitination factors are often involved. Here, three E3 ubiquitin ligases will be reviewed in detail. RNF126, RNF168 and CUL1 are involved in DNA damage response (DDR), DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair, cell cycle regulation, and ultimately, cancer cell proliferation control. Their involvement in multiple cellular pathways makes them an attractive candidate for cancer-targeting therapy. Functional studies of these E3 ligases have increased over the years, and their significance in cancer is well reported. There are continuous efforts to develop drugs targeting the ubiquitin pathway for anticancer therapy, which opens up the possibility for these E3 ligases to be evaluated for their potential as a target protein for anticancer therapy.
Keywords: CUL1; RNF126; RNF168; apoptosis; cell cycle; drug resistance; genome maintenance; targeted cancer therapy; tumor suppressors; ubiquitin pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNF126 Quenches RNF168 Function in the DNA Damage Response.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018 Dec;16(6):428-438. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30529286 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of RNF126 and BCA2 E3 ubiquitin ligases in DNA damage repair signaling and targeted cancer therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2020 May;155:104748. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104748. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32147403 Review.
-
Tumors overexpressing RNF168 show altered DNA repair and responses to genotoxic treatments, genomic instability and resistance to proteotoxic stress.Oncogene. 2017 Apr 27;36(17):2405-2422. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.392. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27841863
-
Ubiquitin E3 ligases in cancer: somatic mutation and amplification.BMB Rep. 2023 May;56(5):265-274. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0037. BMB Rep. 2023. PMID: 37081755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
USP14 regulates DNA damage repair by targeting RNF168-dependent ubiquitination.Autophagy. 2018;14(11):1976-1990. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1496877. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29995557 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

