Eosinophil extracellular traps in asthma: implications for pathogenesis and therapy
- PMID: 37752512
- PMCID: PMC10523707
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-023-02504-4
Eosinophil extracellular traps in asthma: implications for pathogenesis and therapy
Abstract
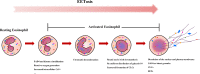
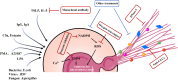
Asthma is a common, chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that affects millions of people worldwide and is associated with significant healthcare costs. Eosinophils, a type of immune cell, play a critical role in the development and progression of asthma. Eosinophil extracellular traps (EETs) are reticular structures composed of DNA, histones, and granulins that eosinophils form and release into the extracellular space as part of the innate immune response. EETs have a protective effect by limiting the migration of pathogens and antimicrobial activity to a controlled range. However, chronic inflammation can lead to the overproduction of EETs, which can trigger and exacerbate allergic asthma. In this review, we examine the role of EETs in asthma.
Keywords: Anti-EETs; Asthma; EETs; Eosinophil extracellular trap cell death; Eosinophil extracellular traps; Therapeutics.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Eosinophil extracellular traps activate type 2 innate lymphoid cells through stimulating airway epithelium in severe asthma.Allergy. 2020 Jan;75(1):95-103. doi: 10.1111/all.13997. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Allergy. 2020. PMID: 31330043
-
Eosinophils release extracellular DNA traps in response to Aspergillus fumigatus.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Feb;141(2):571-585.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.07.048. Epub 2017 Sep 21. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28943470
-
Biological function of eosinophil extracellular traps in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Aug 16;50(8):1-8. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0136-8. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30115903 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophil Extracellular Traps and Inflammatory Pathologies-Untangling the Web!Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 26;9:2763. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02763. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30534130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to detect eosinophil ETosis (EETosis) and extracellular traps.Allergol Int. 2021 Jan;70(1):19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Allergol Int. 2021. PMID: 33189567 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Update on Inflammatory Biomarkers for Defining Asthma Phenotype.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024 Sep;16(5):462-472. doi: 10.4168/aair.2024.16.5.462. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39363766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Respiratory Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 19;13(8):2390. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082390. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presence of sputum IgG against eosinophilic inflammatory proteins in asthma.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1423764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423764. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39091502 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between ROS-inflammatory gene expression axis in the progression of lung disorders.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;398(1):417-448. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03392-1. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39196392 Review.
References
-
- Hammad H, Lambrecht BN. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell. 2021;184(9):2521–2. - PubMed
-
- Dl P, Gy B, Sh K, Ys S, Ym Y, Yj C et al. Neutrophil autophagy and extracellular DNA traps contribute to airway inflammation in severe asthma. Clinical and experimental allergy: journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology [Internet]. 2017 Jan [cited 2022 Jan 5];47(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27883241/. - PubMed
-
- King-Biggs MB, Asthma Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(7):ITC49–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

