CTGF promotes the repair and regeneration of alveoli after acute lung injury by promoting the proliferation of subpopulation of AEC2s
- PMID: 37741976
- PMCID: PMC10517460
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-023-02512-4
CTGF promotes the repair and regeneration of alveoli after acute lung injury by promoting the proliferation of subpopulation of AEC2s
Abstract
Background: Functional alveolar regeneration is essential for the restoration of normal lung homeostasis after acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Lung is a relatively quiescent organ and a variety of stem cells are recruited to participate in lung repair and regeneration after lung tissue injury. However, there is still no effective method for promoting the proliferation of endogenous lung stem cells to promote repair and regeneration.
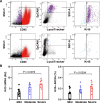
Methods: Using protein mass spectrometry analysis, we analyzed the microenvironment after acute lung injury. RNA sequencing and image cytometry were used in the alveolar epithelial type 2 cells (AEC2s) subgroup identification. Then we used Sftpc+AEC2 lineage tracking mice and purified AEC2s to further elucidate the molecular mechanism by which CTGF regulates AEC2s proliferation both in vitro and in vivo. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from thirty ARDS patients who underwent bronchoalveolar lavage was collected for the analysis of the correlation between the expressing of Krt5 in BALF and patients' prognosis.
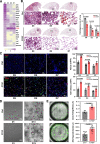
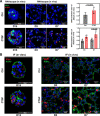
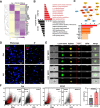
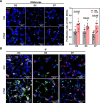
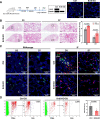
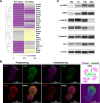
Results: Here, we elucidate that AEC2s are the main facultative stem cells of the distal lung after ALI and ARDS. The increase of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in the microenvironment after ALI promoted the proliferation of AEC2s subpopulations. Proliferated AEC2s rapidly expanded and differentiated into alveolar epithelial type 1 cells (AEC1s) in the regeneration after ALI. CTGF initiates the phosphorylation of LRP6 by promoting the interaction between Krt5 and LRP6 of AEC2s, thus activating the Wnt signaling pathway, which is the molecular mechanism of CTGF promoting the proliferation of AEC2s subpopulation.
Conclusions: Our study verifies that CTGF promotes the repair and regeneration of alveoli after acute lung injury by promoting the proliferation of AEC2s subpopulation.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Acute respiratory distress syndrome; Alveolar epithelial type 1 cells; Alveolar epithelial type 2 cells; Alveolar regeneration; Connective tissue growth factor.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cellular kinetics of lung alveolar epithelial cells and its relationship with lung tissue repair after acute lung injury.Respir Res. 2016 Dec 7;17(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0480-y. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27923370 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo-YAP pathway regulates the proliferation of alveolar epithelial progenitors after acute lung injury.Cell Biol Int. 2019 Oct;43(10):1174-1183. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11098. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Cell Biol Int. 2019. PMID: 30632652
-
Continuous purification and culture of rat type 1 and type 2 alveolar epithelial cells by magnetic cell sorting.Chin J Traumatol. 2022 May;25(3):138-144. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2021.12.005. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Chin J Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 35078688 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between pulmonary epithelial stem cells and innate immune cells contribute to the repair and regeneration of ALI/ARDS.Transl Res. 2024 Oct;272:111-125. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2024.05.012. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38897427 Review.
-
Mechanisms of alveolar epithelial repair in acute lung injury--a translational approach.Swiss Med Wkly. 2003 Nov 22;133(43-44):586-90. doi: 10.4414/smw.2003.10267. Swiss Med Wkly. 2003. PMID: 14745653 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between macrophages and immunometabolism and their potential roles in tissue repair and regeneration.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 18;10(18):e38018. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38018. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39381218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of antibody-mediated connective tissue growth factor neutralization on lung edema in ventilator-induced lung injury in rats.Mol Med. 2024 May 22;30(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00829-4. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38778274 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Regulation of S-Adenosylmethionine on Chondrocytic Differentiation via Stimulation of Polyamine Production and the Gene Expression of Chondrogenic Differentiation Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 9;24(24):17294. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417294. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139122 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82020108021/Key International Cooperation Projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82222038/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CSTB2022NSCQ-JQX0017/Chongqing Outstanding Youth Fund
- 01-SWKJYCJJ06/Outstanding Young Talents of National Defense Biotechnology
- 2022XRC05/Senior Talent Program of the Army Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

