Proteome-wide mendelian randomization study implicates therapeutic targets in common cancers
- PMID: 37735436
- PMCID: PMC10512580
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04525-5
Proteome-wide mendelian randomization study implicates therapeutic targets in common cancers
Abstract
Background: The interest in targeted cancer therapies has been growing rapidly. While numerous cancer biomarkers and targeted treatment strategies have been developed and employed, there are still significant limitations and challenges in the early diagnosis and targeted treatment of cancers. Accordingly, there is an urgent need to identify novel targets and develop new targeted drugs.
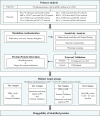
Methods: The study was conducted using combined cis-Mendelian randomization (cis-MR) and colocalization analysis. We analyzed data from 732 plasma proteins to identify potential drug targets associated with eight site-specific cancers. These findings were further validated using the UK Biobank dataset. Then, a protein-protein interaction network was also constructed to examine the interplay between the identified proteins and the targets of existing cancer medications.
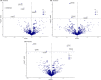
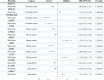
Results: This MR analysis revealed associations between five plasma proteins and prostate cancer, five with breast cancer, and three with lung cancer. Subsequently, these proteins were classified into four distinct target groups, with a focus on tier 1 and 2 targets due to their higher potential to become drug targets. Our study indicatied that genetically predicted KDELC2 (OR: 0.89, 95% CI 0.86-0.93) and TNFRSF10B (OR: 0.74, 95% CI 0.65-0.83) are inversely associated with prostate cancer. Furthermore, we observed an inverse association between CPNE1 (OR: 0.96, 95% CI 0.94-0.98) and breast cancer, while PDIA3 (OR: 1.19, 95% CI 1.10-1.30) were found to be associated with the risk of breast cancer. In addition, we also propose that SPINT2 (OR: 1.05, 95% CI 1.03-1.06), GSTP1 (OR: 0.82, 95% CI 0.74-0.90), and CTSS (OR: 0.91, 95% CI 0.88-0.95) may serve as potential therapeutic targets in prostate cancer. Similarly, GDI2 (OR: 0.85, 95% CI 0.80-0.91), ISLR2 (OR: 0.87, 95% CI 0.82-0.93), and CTSF (OR: 1.14, 95% CI 1.08-1.21) could potentially be targets for breast cancer. Additionally, we identified SFTPB (OR: 0.93, 95% CI 0.91-0.95), ICAM5 (OR: 0.95, 95% CI 0.93-0.97), and FLRT3 (OR: 1.10, 95% CI 1.05-1.15) as potential targets for lung cancer. Notably, TNFRSF10B, GSTP1, and PDIA3 were found to interact with the target proteins of current medications used in prostate or breast cancer treatment.
Conclusions: This comprehensive analysis has highlighted thirteen plasma proteins with potential roles in three site-specific cancers. Continued research in this area may reveal their therapeutic potential, particularly KDELC2, TNFRSF10B, CPNE1, and PDIA3, paving the way for more effective cancer treatments.
Keywords: Cancers; Drug target prediction; Mendelian randomization; Protein quantitative trait loci.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this section.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic proteome-wide Mendelian randomization using the human plasma proteome to identify therapeutic targets for lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2024 Apr 4;22(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04919-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38576019 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying new biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for breast cancer through the integration of human plasma proteomics: a Mendelian randomization study and colocalization analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 16;15:1449668. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1449668. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39351539 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-Wide Multicenter Mendelian Randomization Analysis to Identify Novel Therapeutic Targets for Lung Cancer.Arch Bronconeumol. 2024 Sep;60(9):553-558. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2024.05.007. Epub 2024 May 16. Arch Bronconeumol. 2024. PMID: 38824092 English, Spanish.
-
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review of Mendelian Randomization Studies.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 13;15(2):422. doi: 10.3390/nu15020422. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Dichotomy of Urinary Proteins: Diagnostic Insights into Breast and Prostate Cancer and Their Roles.Proteomes. 2023 Dec 26;12(1):1. doi: 10.3390/proteomes12010001. Proteomes. 2023. PMID: 38250812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the susceptibility to breast cancer: an in-depth proteomic and transcriptomic investigation into novel potential plasma protein biomarkers.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 18;10:1340917. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1340917. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38304232 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of ICAM5 in Carcinostasis Effects on LUAD Based on the ROS1-Related Prognostic Model.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep 20;17:6583-6602. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S475088. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39318995 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Protein Biomarkers and Drug Targets for Acne Vulgaris by Integrating Human Plasma Proteome with Genome-Wide Association Data.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 9;17:4431-4441. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S463450. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39006495 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic proteome-wide Mendelian randomization using the human plasma proteome to identify therapeutic targets for lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2024 Apr 4;22(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04919-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38576019 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter proteome-wide Mendelian randomization study identifies causal plasma proteins in melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers.Commun Biol. 2024 Jul 13;7(1):857. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06538-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39003418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, Fu W, Gaw BL, Harvey JD, et al. Cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life years for 29 cancer groups from 2010 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(3):420–444. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.6987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

