Prenatal FGFR2 Signaling via PI3K/AKT Specifies the PDGFRA+ Myofibroblast
- PMID: 37734036
- PMCID: PMC10768833
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0245OC
Prenatal FGFR2 Signaling via PI3K/AKT Specifies the PDGFRA+ Myofibroblast
Abstract
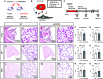
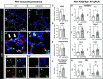
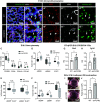
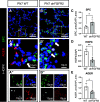
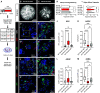
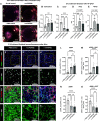
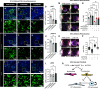
It is well known that FGFR2 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 2) signaling is critical for proper lung development. Recent studies demonstrate that epithelial FGFR2 signaling during the saccular phase of lung development (sacculation) regulates alveolar type 1 (AT1) and AT2 cell differentiation. During sacculation, PDGFRA (platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α)-positive lung fibroblasts exist as three functional subtypes: contractile myofibroblasts, extracellular matrix-producing matrix fibroblasts, and lipofibroblasts. All three subtypes are required during alveolarization to establish a niche that supports AT2 epithelial cell self-renewal and AT1 epithelial cell differentiation. FGFR2 signaling directs myofibroblast differentiation in PDGFRA+ fibroblasts during alveolar reseptation after pneumonectomy. However, it remains unknown if FGFR2 signaling regulates PDGFRA+ myo-, matrix, or lipofibroblast differentiation during sacculation. In this study, FGFR2 signaling was inhibited by temporal expression of a secreted dominant-negative FGFR2b (dnFGFR2) by AT2 cells from embryonic day (E) 16.5 to E18.5. Fibroblast and epithelial differentiation were analyzed at E18.5 and postnatal days 7 and 21. At all time points, the number of myofibroblasts was reduced and the number of lipo-/matrix fibroblasts was increased. AT2 cells are increased and AT1 cells are reduced postnatally, but not at E18.5. Similarly, in organoids made with PDGFRA+ fibroblasts from dnFGFR2 lungs, increased AT2 cells and reduced AT1 cells were observed. In vitro treatment of primary wild-type E16.5 adherent saccular lung fibroblasts with recombinant dnFGFR2b/c resulted in reduced myofibroblast contraction. Treatment with the PI3K/AKT activator 740 Y-P rescued the lack of myofibroblast differentiation caused by dnFGFR2b/2c. Moreover, treatment with the PI3K/AKT activator 740 Y-P rescued myofibroblast differentiation in E18.5 fibroblasts isolated from dnFGFR2 lungs.
Keywords: alveolar niche; lipofibroblast; lung development; matrix fibroblast; sacculation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hedgehog and Platelet-derived Growth Factor Signaling Intersect during Postnatal Lung Development.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023 May;68(5):523-536. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2022-0269OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36693140 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor α expression in alveolar fibroblasts during realveolarization.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Oct;47(4):517-27. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0030OC. Epub 2012 May 31. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22652199 Free PMC article.
-
Maladaptive functional changes in alveolar fibroblasts due to perinatal hyperoxia impair epithelial differentiation.JCI Insight. 2022 Mar 8;7(5):e152404. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.152404. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35113810 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal, spatial, and phenotypical changes of PDGFRα expressing fibroblasts during late lung development.Dev Biol. 2017 May 15;425(2):161-175. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.03.020. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28408205 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent fibroblast growth factor signaling pathways in lung fibroblast subsets: where do we go from here?Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Oct 15;309(8):L751-5. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00298.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26342090 Review.
References
-
- Burri PH, Dbaly J, Weibel ER. The postnatal growth of the rat lung. I. Morphometry. Anat Rec . 1974;178:711–730. - PubMed
-
- Northway WH, Jr, Rosan RC, Porter DY. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med . 1967;276:357–368. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

