Identification of histone deacetylase inhibitors as neutrophil recruitment modulators in zebrafish using a chemical library screen
- PMID: 37728477
- PMCID: PMC10621070
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.050056
Identification of histone deacetylase inhibitors as neutrophil recruitment modulators in zebrafish using a chemical library screen
Abstract
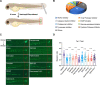
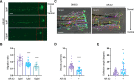
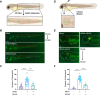
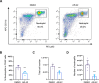
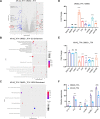
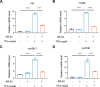
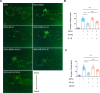
Tissue injury-induced neutrophil recruitment is a prerequisite for the initiation and amplification of inflammatory responses. Although multiple proteases and enzymes involved in post-translational modification (PTM) of proteins regulate leukocyte recruitment, an unbiased functional screen of enzymes regulating inflammatory leukocyte recruitment has yet to be undertaken. Here, using a zebrafish tail fin amputation (TFA) model to screen a chemical library consisting of 295 compounds that target proteases and PTM enzymes, we identified multiple histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors that modulate inflammatory neutrophil recruitment. AR-42, a pan-HDAC inhibitor, was shown to inhibit neutrophil recruitment in three different zebrafish sterile tissue injury models: a TFA model, a copper-induced neuromast damage and mechanical otic vesicle injury (MOVI) model, and a sterile murine peritonitis model. RNA sequencing analysis of AR-42-treated fish embryos revealed downregulation of neutrophil-associated cytokines/chemokines, and exogenous supplementation with recombinant human IL-1β and CXCL8 partially restored the defective neutrophil recruitment in AR-42-treated MOVI model fish embryos. We thus demonstrate that AR-42 non-cell-autonomously modulates neutrophil recruitment by suppressing transcriptional expression of cytokines/chemokines, thereby identifying AR-42 as a promising anti-inflammatory drug for treating sterile tissue injury-associated diseases.
Keywords: AR-42; Cell migration; HDAC; Neutrophil; Zebrafish.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitors of neutrophil recruitment identified using transgenic zebrafish to screen a natural product library.Dis Model Mech. 2014 Jan;7(1):163-9. doi: 10.1242/dmm.012047. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Dis Model Mech. 2014. PMID: 24291762 Free PMC article.
-
Cxcl8 (IL-8) mediates neutrophil recruitment and behavior in the zebrafish inflammatory response.J Immunol. 2013 Apr 15;190(8):4349-59. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203266. Epub 2013 Mar 18. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23509368 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota metabolite butyrate constrains neutrophil functions and ameliorates mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease.Gut Microbes. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1968257. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1968257. Gut Microbes. 2021. PMID: 34494943 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Chemokines and Cytokines by Histone Deacetylases and an Update on Histone Decetylase Inhibitors in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 5;20(5):1110. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051110. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30841513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular choreography of neutrophil recruitment to sites of sterile inflammation.J Mol Med (Berl). 2011 Nov;89(11):1079-88. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0784-9. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21751029 Review.
References
-
- Bertolotto, M., Contini, P., Ottonello, L., Pende, A., Dallegri, F. and Montecucco, F. (2014). Neutrophil migration towards C5a and CXCL8 is prevented by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs via inhibition of different pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 171, 3376-3393. 10.1111/bph.12670 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng, Y., Zhao, J., Tse, H. F., Le, X. C. and Rong, J. (2015). Plant Natural products calycosin and gallic acid synergistically attenuate neutrophil infiltration and subsequent injury in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction: a possible role for leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 434052. 10.1155/2015/434052 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

