Compassionate Use of Remdesivir in Pregnancy: A Case Series From a COVID-19 Dedicated Center and Review of Literature
- PMID: 37727185
- PMCID: PMC10506363
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.43671
Compassionate Use of Remdesivir in Pregnancy: A Case Series From a COVID-19 Dedicated Center and Review of Literature
Abstract
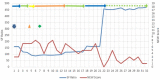
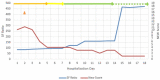
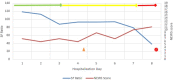
Pregnancy is associated with immunological changes that could render an individual vulnerable to the severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) disease. Even as we witnessed the third and most widespread pandemic wave, a conclusively advantageous treatment option still remained elusive. Remdesivir was one of the front-running therapeutic options that received emergency use authorization (EUA) and subsequent approval for the management of moderate to severe COVID-19 infections. Here, we report a series of moderate to severe COVID-19-infected pregnancies and the experience of remdesivir use on a compassionate basis. Four cases of pregnancy complicated with moderate to severe COVID-19 infections where remdesivir was administered were recruited into the study, and their outcome was assessed objectively. Of these cases, three women received remdesivir in addition to standard SARS-CoV-2 treatment in the antenatal period. One woman received remdesivir after delivery. One woman received tocilizumab in addition to remdesivir and standard SARS-CoV-2 care. Two women survived and were subsequently discharged to home care. Two succumbed to the disease. One baby who was exposed to remdesivir in utero is doing well at six months post-delivery. Remdesivir had been granted EUA for the treatment of suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 infection in adults and children who were hospitalized with severe disease or requiring supplemental oxygen and mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in May 2020. This issuance allowed the use of the same dosing regimen in pregnant and parturient women as in the general adult population. Thus, this series of cases tried to assess the outcome of this drug among COVID-19-infected pregnant women. Early initiation of remdesivir in pregnancy in the viremic phase seems to provide some advantages in the survival outcome. Its use may be associated with transient elevation in hepatic transaminases in some cases. No detrimental effects on the ongoing pregnancies, fetuses, or neonates have been observed. Further large-scale studies may provide more conclusive evidence.
Keywords: covid-19; pregnancy; prone positioning; remdesivir; sars-cov-2; tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2023, Sharma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatment in pregnant women with moderate symptoms of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Dec;35(25):5970-5977. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2021.1903426. Epub 2021 Mar 26. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022. PMID: 33771091
-
A Phase I/II Clinical Trial to evaluate the efficacy of baricitinib to prevent respiratory insufficiency progression in onco-hematological patients affected with COVID19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Feb 5;22(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05072-4. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33546739 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and pregnancy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun;222(6):521-531. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.03.021. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32217113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal outcomes of pregnant women with severe COVID-19 requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO): a case series and literature review.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022 May;305(5):1135-1142. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06479-3. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 35262778 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID 19) Dashboard. [ Feb; 2022 ]. 2020. https://coronavirus/vaccine/summary-of-yellow-card-reporting/files/COVID... https://coronavirus/vaccine/summary-of-yellow-card-reporting/files/COVID...
-
- Management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia. Thirkell P, Griffiths M, Waller MD. Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine. 2021:342–349.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
