Smart and versatile biomaterials for cutaneous wound healing
- PMID: 37717028
- PMCID: PMC10504797
- DOI: 10.1186/s40824-023-00426-2
Smart and versatile biomaterials for cutaneous wound healing
Abstract
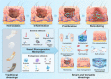
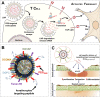
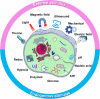
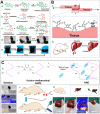
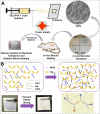
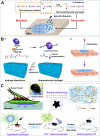
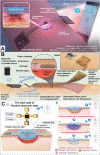
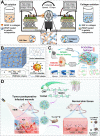
The global increase of cutaneous wounds imposes huge health and financial burdens on patients and society. Despite improved wound healing outcomes, conventional wound dressings are far from ideal, owing to the complex healing process. Smart wound dressings, which are sensitive to or interact with changes in wound condition or environment, have been proposed as appealing therapeutic platforms to effectively facilitate wound healing. In this review, the wound healing processes and features of existing biomaterials are firstly introduced, followed by summarizing the mechanisms of smart responsive materials. Afterwards, recent advances and designs in smart and versatile materials of extensive applications for cutaneous wound healing were submarined. Finally, clinical progresses, challenges and future perspectives of the smart wound dressing are discussed. Overall, by mapping the composition and intrinsic structure of smart responsive materials to their individual needs of cutaneous wounds, with particular attention to the responsive mechanisms, this review is promising to advance further progress in designing smart responsive materials for wounds and drive clinical translation.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Smart dressings; Stimuli-responsive; Wound healing.
© 2023. The Korean Society for Biomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Wound Healing: From Passive to Smart Dressings.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Aug;10(16):e2100477. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202100477. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 34174163 Review.
-
Research advances in smart responsive-hydrogel dressings with potential clinical diabetic wound healing properties.Mil Med Res. 2023 Aug 23;10(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00473-9. Mil Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37608335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of Smart Biomaterials for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing.Molecules. 2023 Jan 22;28(3):1110. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031110. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymer-based biomaterials for chronic wound management: Promises and challenges.Int J Pharm. 2021 Apr 1;598:120270. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120270. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33486030 Review.
-
Next-generation of smart dressings: Integrating multiplexed sensors and theranostic functions.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;254(Pt 1):127737. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127737. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38287589 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomedical Applications of CNT-Based Fibers.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 7;14(3):137. doi: 10.3390/bios14030137. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Immobilization on Bacterial Cellulose for Biomedical Application.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;16(17):2468. doi: 10.3390/polym16172468. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39274101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Halloysite Nanohybrids-Based Films: Enhancing Mechanical and Hydrophilic Properties for Wound Healing.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 27;16(10):1258. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101258. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458589 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and hot topics of wearable sensors in wound care over past 18 years: A bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 30;10(20):e38762. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38762. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39512323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saghazadeh S, Rinoldi C, Schot M, Kashaf SS, Sharifi F, Jalilian E, Nuutila K, Giatsidis G, Mostafalu P, Derakhshandeh H, Yue K, Swieszkowski W, Memic A, Tamayol A, Khademhosseini A. Drug delivery systems and materials for wound healing applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;127:138–66. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim HS, Sun X, Lee JH, Kim HW, Fu X, Leong KW. Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146:209–39. - PubMed
-
- Abbas O, Mahalingam M. Epidermal stem cells: practical perspectives and potential uses. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161(2):228–36. - PubMed
-
- Farahani M, Shafiee A. Wound Healing: from Passive to Smart Dressings. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(16):e2100477. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82072177/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 'Two Hundred Talent' Program/'Two Hundred Talent' Program
- 'Outstanding Youth Medical Talents' Shanghai 'Rising Stars of Medical Talent' Youth Development Program/'Outstanding Youth Medical Talents' Shanghai 'Rising Stars of Medical Talent' Youth Development Program
- shslczdzk00901/the first Continuous Outstanding Special Technology Supporting Project and Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

