Nanoparticle-based delivery systems as emerging therapy in retinoblastoma: recent advances, challenges and prospects
- PMID: 37705787
- PMCID: PMC10496918
- DOI: 10.1039/d3na00462g
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems as emerging therapy in retinoblastoma: recent advances, challenges and prospects
Abstract
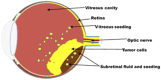
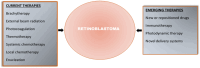
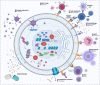
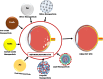
Retinoblastoma is the most common intraocular malignancy in children. The treatment of this rare disease is still challenging in developing countries due to delayed diagnosis. The current therapies comprise mainly surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The adverse effects of radiation and chemotherapeutic drugs have been reported to contribute to the high mortality rate and affect patients' quality of life. The systemic side effects resulting from the distribution of chemotherapeutic drugs to non-cancerous cells are enormous and have been recognized as one of the reasons why most potent anticancer compounds fail in clinical trials. Nanoparticulate delivery systems have the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment by offering targeted delivery, enhanced penetration and retention effects, increased bioavailability, and an improved toxicity profile. Notwithstanding the plethora of evidence on the beneficial effects of nanoparticles in retinoblastoma, the clinical translation of this carrier is yet to be given the needed attention. This paper reviews the current and emerging treatment options for retinoblastoma, with emphasis on recent investigations on the use of various classes of nanoparticles in diagnosing and treating retinoblastoma. It also presents the use of ligand-conjugated and smart nanoparticles in the active targeting of anticancer and imaging agents to the tumour cells. In addition, this review discusses the prospects and challenges in translating this nanocarrier into clinical use for retinoblastoma therapy. This review may provide new insight for formulation scientists to explore in order to facilitate the development of more effective and safer medicines for children suffering from retinoblastoma.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-mediated gene therapy as a novel strategy for the treatment of retinoblastoma.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022 Dec;220:112899. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112899. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022. PMID: 36252537 Review.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
-
Multi-Functionalized Nanomaterials and Nanoparticles for Diagnosis and Treatment of Retinoblastoma.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 26;11(4):97. doi: 10.3390/bios11040097. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33810621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
Current therapy and recent advances in the management of retinoblastoma.Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2012 Apr;33(2):80-8. doi: 10.4103/0971-5851.99731. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22988349 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advancing biomedical applications: an in-depth analysis of silver nanoparticles in antimicrobial, anticancer, and wound healing roles.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 8;15:1438227. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1438227. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39175537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

