Mechanism of ozone alleviation of malignant ascites in hepatocellular carcinoma through the inhibition of neutrophil extracellular traps
- PMID: 37693209
- PMCID: PMC10485884
- DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad280
Mechanism of ozone alleviation of malignant ascites in hepatocellular carcinoma through the inhibition of neutrophil extracellular traps
Abstract
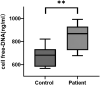
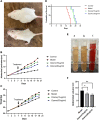
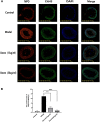
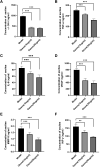
Malignant ascites in hepatocellular carcinoma is usually a sign of advanced disease and poor prognosis and is also thought to be associated with chronic inflammation mediated by neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) networks. Although ozone, a strong oxidant, has significant antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, its effectiveness in treating malignant liver ascites is unclear. We first measured the levels of NETs in the peripheral blood of patients with liver cancer and healthy individuals. Next, we constructed the H22 tumor-bearing mouse model and observed the abdominal girth, body weight, survival rate, and survival time in each group; we marked the proteins associated with NETs in mouse intestinal tissues by immunofluorescence; cf-DNA and cytokines in ascites such as: tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), interleukin 6 (IL-6), matrix metalloprotein 9 (MMP-9), and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels in ascites were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The expression levels of phosphorylated adenylate-activated protein kinase (P-AMPK) and scavenger receptor-A (SR-A) were detected by immunocytochemistry in the intestinal tissues of each group of mice. We further examined the expression of P-AMPK and SR-A proteins in ascites deposits by Western blotting. The results show, the plasma levels of NETs were higher in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma than in normal subjects (P < 0.01). Abdominal girth and body weight were significantly reduced in the ozone-treated group compared with the model group, while survival and survival time were dose dependently increased (both P < 0.05). NET-associated guanine histone H3 and myeloperoxidase were abundantly expressed at neutrophil aggregates in the intestinal tissues of the model mice, whereas their expression was significantly reduced in the ozone-treated group. The levels of cf-DNA, IL-6, IFN-γ, MMP-9, VEGF, and TNF-α were dose dependently increased in the ascites of H22 tumor-bearing mice in the ozone-treated group compared with the model group (all P < 0.01), while the expression of P-AMPK and SR-A proteins was increased in the ozone-treated group compared with the model group. Ozone showed significant antiperitoneal fluid production properties in H22 tumor-bearing mice, and ozone reduced peritoneal fluid production by activating AMPK and up-regulating SR-A phagocytosis damage-associated molecular patterns to reduce the production of NETs. This suggests that ozone could be used as a new drug for the treatment of malignant ascites in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma ascites; neutrophil extracellular trap network; ozone.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of National Academy of Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ozone enhances the efficacy of radiation therapy in esophageal cancer.J Radiat Res. 2024 Jul 22;65(4):467-473. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrae041. J Radiat Res. 2024. PMID: 38842109 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides Extracted from Rhizoma Pleionis Have Antitumor Properties In Vitro and in an H22 Mouse Hepatoma Ascites Model In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 7;19(5):1386. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051386. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29735884 Free PMC article.
-
[Dermatophagoides farinae induces conjunctival epithelial cell damage to promote neutrophil migration and neutrophil extracellular traps formation].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2023 Jul 4;35(3):271-278. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2023032. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37455098 Chinese.
-
The therapeutic function of the chemokine RANTES on the H22 hepatoma ascites model.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Aug;367(1-2):93-102. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1323-x. Epub 2012 May 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22547199
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Sustain Inflammatory Signals in Ulcerative Colitis.J Crohns Colitis. 2019 May 27;13(6):772-784. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy215. J Crohns Colitis. 2019. PMID: 30715224
Cited by
-
Ozone enhances the efficacy of radiation therapy in esophageal cancer.J Radiat Res. 2024 Jul 22;65(4):467-473. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrae041. J Radiat Res. 2024. PMID: 38842109 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1+ neutrophils induced NETs in malignant ascites is a potential biomarker in HCC.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Oct 3;73(12):254. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03833-z. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39358478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jehn CF, Küpferling S, Oskay-Özcelik G, Lüftner D. 2015. A survey of treatment approaches of malignant ascites in Germany and Austria. Support Care Cancer. 23:2073–2078. - PubMed
-
- Enck RE. 2002. Malignant ascites. Am J Hosp Palliat Med. 19(1):7–8. - PubMed
-
- Becker G, Galandi D, Blum HE. 2006. Malignant ascites: systematic review and guideline for treatment. Eur J Cancer. 42(5):589–597. - PubMed
-
- Chung M, Kozuch P. 2008. Treatment of malignant ascites. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 9:215–233. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

