Genome-Wide Characterization of Soybean Hexokinase Genes Reveals a Positive Role of GmHXK15 in Alkali Stress Response
- PMID: 37687370
- PMCID: PMC10490225
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12173121
Genome-Wide Characterization of Soybean Hexokinase Genes Reveals a Positive Role of GmHXK15 in Alkali Stress Response
Abstract
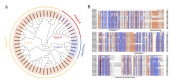
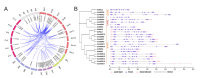
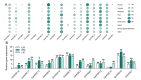
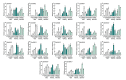
Hexokinase (HXK) proteins catalyze hexose phosphorylation and are important for the sensing and signaling of sugar. In order to determine the roles played by HXKs in soybean growth and stress responsiveness, seventeen HXK genes (GmHXK1-17) were isolated and analyzed. The phylogenic analysis and subcellular location prediction showed that GmHXKs were clearly classified into type A (GmHXK1-4) and type B (GmHXK5-17). There were similar protein structures and conserved regions in GmHXKs to the HXKs of other plants. An expression analysis of the GmHXK genes in soybean organs or tissues demonstrated that GmHXK3 and GmHXK12, 15, and 16 were the dominant HXKs in all the examined tissues. In addition, salt, osmotic, and alkaline stress treatments dramatically increased the activity and transcripts of GmHXKs. There is the possibility that a type-B isoform (GmHXK15) plays a crucial role in soybean adaptation to alkali, as the expression levels of this isoform correlate well with the HXK enzyme activity. Based on an enzyme assay performed on recombinant plant HXK15 proteins expressed in Escherichia coli, we found that GmHXK15 had functional HXK activities. A further analysis indicated that GmHXK15 specifically targeted the mitochondria, and the overexpression of the GmHXK15 gene could significantly enhance the resistance of transgenic soybean to alkali stress. The present findings will serve as a basis for a further analysis of the function of the GmHXK gene family.
Keywords: abiotic stress; enzyme activity; expression; hexokinase; soybean (Glycine max L.).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of hexokinase gene family members in Glycine max and functional analysis of GmHXK2 under salt stress.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 23;14:1135290. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1135290. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36911414 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Expression, and Functional Analysis of the Hexokinase Gene Family in Cassava.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 12;18(5):1041. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051041. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28498327 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Family in Soybean and Functional Identification of GmG6PDH2 Involvement in Salt Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 26;11:214. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00214. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32174950 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Hexokinases are Multifaceted Proteins.Plant Cell Physiol. 2017 Jul 1;58(7):1151-1160. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx062. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28449056 Review.
-
Putting plant hexokinases in their proper place.Phytochemistry. 2008 Nov;69(15):2649-54. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.08.026. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Phytochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18922551 Review.
Cited by
-
The critical roles of three sugar-related proteins (HXK, SnRK1, TOR) in regulating plant growth and stress responses.Hortic Res. 2024 Apr 4;11(6):uhae099. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae099. eCollection 2024 Jun. Hortic Res. 2024. PMID: 38863993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bezrutczyk M., Yang J., Eom J., Prior M., Sosso D., Hartwig T., Szurek B., Oliva R., Vera-Cruz C., White F.F., et al. Sugar flux and signaling in plant-microbe interactions. Plant J. 2018;93:675–685. - PubMed
-
- Rolland F., Baena-Gonzalez E., Sheen J. Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: Conserved and novel mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006;57:675–709. - PubMed
-
- Granot D., Kelly G., Stein O., David-Schwartz R. Substantial roles of hexokinase and fructokinase in the effects of sugars on plant physiology and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2014;65:809–819. - PubMed
-
- Claeyssen E., Rivoal J. Isozymes of plant hexokinase: Occurrence, properties and functions. Phytochemistry. 2007;68:709–731. - PubMed
-
- Sami F., Siddiqui H., Hayat S. Interaction of glucose and phytohormone signaling in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019;135:119–126. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

