Lipid metabolism transcriptomics of murine microglia in Alzheimer's disease and neuroinflammation
- PMID: 37684405
- PMCID: PMC10491618
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41897-6
Lipid metabolism transcriptomics of murine microglia in Alzheimer's disease and neuroinflammation
Abstract
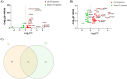
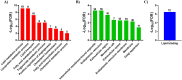
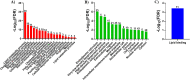
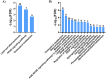
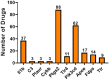
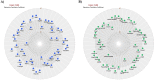
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques followed by intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) composed of hyperphosphorylated tau. An unrestrained immune response by microglia, the resident cells of the central nervous system (CNS), leads to neuroinflammation which can amplify AD pathology. AD pathology is also driven by metabolic dysfunction with strong correlations between dementia and metabolic disorders such as diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertriglyceridemia. Since elevated cholesterol and triglyceride levels appear to be a major risk factor for developing AD, we investigated the lipid metabolism transcriptome in an AD versus non-AD state using RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) and microarray datasets from N9 cells and murine microglia. We identified 52 differentially expressed genes (DEG) linked to lipid metabolism in LPS-stimulated N9 microglia versus unstimulated control cells using RNA-seq, 86 lipid metabolism DEG in 5XFAD versus wild-type mice by microarray, with 16 DEG common between both datasets. Functional enrichment and network analyses identified several biological processes and molecular functions, such as cholesterol homeostasis, insulin signaling, and triglyceride metabolism. Furthermore, therapeutic drugs targeting lipid metabolism DEG found in our study were identified. Focusing on drugs that target genes associated with lipid metabolism and neuroinflammation could provide new targets for AD drug development.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional response of murine microglia in Alzheimer's disease and inflammation.BMC Genomics. 2022 Mar 5;23(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08417-8. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35247975 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of murine interferon genes in microglial-mediated neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroimmunol. 2023 Feb 15;375:578031. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2023.578031. Epub 2023 Jan 21. J Neuroimmunol. 2023. PMID: 36708632 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the zinc-related transcriptional landscape in Alzheimer's disease.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Jun 7;13:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.06.002. eCollection 2022 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35711243 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc utilization by microglia in Alzheimer's disease.J Biol Chem. 2024 May;300(5):107306. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107306. Epub 2024 Apr 20. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38648940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional and Phenotypic Diversity of Microglia: Implication for Microglia-Based Therapies for Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 May 26;14:896852. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.896852. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35693341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SCGB1A1 as a novel biomarker and promising therapeutic target for the management of HNSCC.Oncol Lett. 2024 Sep 3;28(5):527. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14660. eCollection 2024 Nov. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39268163 Free PMC article.
-
AIBP controls TLR4 inflammarafts and mitochondrial dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 27:2024.02.16.580751. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.16.580751. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Sep 28;21(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03214-4. PMID: 38586011 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Minding the Gap: Exploring Neuroinflammatory and Microglial Sex Differences in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 12;24(24):17377. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417377. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro biological studies and computational prediction-based analyses of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives.RSC Adv. 2024 Mar 12;14(12):8397-8408. doi: 10.1039/d4ra00423j. eCollection 2024 Mar 6. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38476172 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of gut microbiota dynamics in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model through clade-specific marker-based analysis of shotgun metagenomic data.Biol Direct. 2024 Oct 30;19(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00541-7. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 39478626 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

