Trinity of inflammation, innate immune cells and cross-talk of signalling pathways in tumour microenvironment
- PMID: 37680708
- PMCID: PMC10482416
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1255727
Trinity of inflammation, innate immune cells and cross-talk of signalling pathways in tumour microenvironment
Abstract
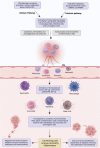
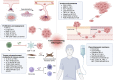
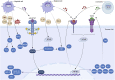
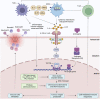
Unresolved inflammation is a pathological consequence of persistent inflammatory stimulus and perturbation in regulatory mechanisms. It increases the risk of tumour development and orchestrates all stages of tumorigenesis in selected organs. In certain cancers, inflammatory processes create the appropriate conditions for neoplastic transformation. While in other types, oncogenic changes pave the way for an inflammatory microenvironment that leads to tumour development. Of interest, hallmarks of tumour-promoting and cancer-associated inflammation are striking similar, sharing a complex network of stromal (fibroblasts and vascular cells) and inflammatory immune cells that collectively form the tumour microenvironment (TME). The cross-talks of signalling pathways initially developed to support homeostasis, change their role, and promote atypical proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, and subversion of adaptive immunity in TME. These transcriptional and regulatory pathways invariably contribute to cancer-promoting inflammation in chronic inflammatory disorders and foster "smouldering" inflammation in the microenvironment of various tumour types. Besides identifying common target sites of numerous cancer types, signalling programs and their cross-talks governing immune cells' plasticity and functional diversity can be used to develop new fate-mapping and lineage-tracing mechanisms. Here, we review the vital molecular mechanisms and pathways that establish the connection between inflammation and tumour development, progression, and metastasis. We also discussed the cross-talks between signalling pathways and devised strategies focusing on these interaction mechanisms to harness synthetic lethal drug combinations for targeted cancer therapy.
Keywords: cross-talks; inflammation; innate immunity; signalling pathways; tumorigenesis; tumour microenvironment; tumour-promoting inflammation.
Copyright © 2023 Attiq and Afzal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Tumour-Associated Fibroblasts in Cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 22;12:908156. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.908156. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35814453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: Critical Mediators of Tumour Microenvironment Reprogramming.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(39):8182-8202. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666201217105529. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33334279 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and colorectal cancer: a troublesome twosome for the anti-tumour immune response?Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):60752-60774. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11354. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27542276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating Tumour Microenvironment and Wnt Signalling Crosstalk: Implications for Advanced Cancer Therapeutics.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;15(24):5847. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245847. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity and gastrointestinal cancer: the interrelationship of adipose and tumour microenvironments.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Nov;15(11):699-714. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0069-7. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30323319 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine Storm-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction in COVID-19: Insights into Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approaches.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Sep 20;18:4215-4240. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S475005. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39319193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Inflammatory Phenotype in Mice Deficient in Fibulin-2 and ADAMTS-12.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 7;25(4):2024. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042024. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afzal S., Abdul Sattar M., Johns E. J., Eseyin O. A. (2020). Renoprotective and haemodynamic effects of adiponectin and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist, pioglitazone, in renal vasculature of diabetic Spontaneously hypertensive rats. PLoS One 15, e0229803. 10.1371/journal.pone.0229803 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

