B cell metabolism in autoimmune diseases: signaling pathways and interventions
- PMID: 37680644
- PMCID: PMC10481957
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1232820
B cell metabolism in autoimmune diseases: signaling pathways and interventions
Abstract
Autoimmune diseases are heterogeneous disorders believed to stem from the immune system's inability to distinguish between auto- and foreign- antigens. B lymphocytes serve a crucial role in humoral immunity as they generate antibodies and present antigens. Dysregulation of B cell function induce the onset of autoimmune disorders by generating autoantibodies and pro-inflammatory cytokines, resulting in an imbalance in immune regulation. New research in immunometabolism shows that cellular metabolism plays an essential role in controlling B lymphocytes immune reactions by providing the energy and substrates for B lymphocytes activation, differentiation, and function. However, dysregulated immunometabolism lead to autoimmune diseases by disrupting self-tolerance mechanisms. This review summarizes the latest research on metabolic reprogramming of B lymphocytes in autoimmune diseases, identifying crucial pathways and regulatory factors. Moreover, we consider the potential of metabolic interventions as a promising therapeutic strategy. Understanding the metabolic mechanisms of B cells brings us closer to developing novel therapies for autoimmune disorders.
Keywords: B cell; B cell differentiation and function; B cell metabolism; autoimmune diseases; autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Zhao, Luo, Huang, Zhao and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
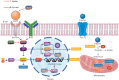

Similar articles
-
The role of B cell metabolism in autoimmune diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2022 Jul;21(7):103116. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2022.103116. Epub 2022 May 17. Autoimmun Rev. 2022. PMID: 35595053 Review.
-
Intracellular B Lymphocyte Signalling and the Regulation of Humoral Immunity and Autoimmunity.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Oct;53(2):237-264. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8609-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28456914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B Cell-Mediated Autoimmune Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1254:145-160. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3532-1_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32323275 Review.
-
Impaired B-cell tolerance checkpoints promote the development of autoimmune diseases and pathogenic autoantibodies.Immunol Rev. 2019 Nov;292(1):90-101. doi: 10.1111/imr.12821. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31721234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting B cells and autoantibodies in the therapy of autoimmune diseases.Semin Immunopathol. 2014 May;36(3):289-99. doi: 10.1007/s00281-014-0427-7. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Semin Immunopathol. 2014. PMID: 24777745 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of Sjögren's syndrome: Classification criteria, risk factors, and signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 15;10(17):e36220. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36220. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39286095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Clock Perspective in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Inflammation. 2024 Aug 10. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02120-4. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39126449 Review.
-
Metabolic imbalance driving immune cell phenotype switching in autoimmune disorders: Tipping the balance of T- and B-cell interactions.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Mar;14(3):e1626. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1626. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38500390 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

