Integrated Analysis of Non-Coding RNA and mRNA Expression Profiles in Exosomes from Lung Tissue with Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- PMID: 37674532
- PMCID: PMC10478974
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S419491
Integrated Analysis of Non-Coding RNA and mRNA Expression Profiles in Exosomes from Lung Tissue with Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) is associated with a high mortality rate; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression profile and related networks of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and mRNAs in lung tissue exosomes obtained from sepsis-induced ALI.
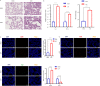
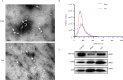
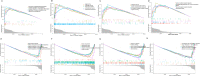
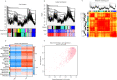
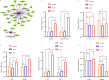
Methods: A mouse model of sepsis was established using the cecal ligation and puncture method. RNA sequencing was performed using lung tissue exosomes obtained from mice in the sham and CLP groups. Hematoxylin-eosin staining, Western blotting, immunofluorescence, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and nanoparticle tracking analysis were performed to identify relevant phenotypes, and bioinformatic algorithms were used to evaluate competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks.
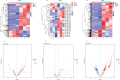
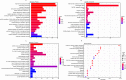
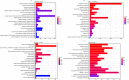
Results: Thirty lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA interactions were identified, including two upregulated lncRNAs, 30 upregulated miRNAs, and two downregulated miRNAs. Based on the expression levels of differentially expressed mRNAs(DEmRNAs), differentially expressed LncRNAs(DELncRNAs), and differentially expressed miRNAs(DEmiRNAs), 30 ceRNA networks were constructed.
Conclusion: Our study revealed, for the first time, the expression profiles of lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in exosomes isolated from the lungs of mice with sepsis-induced ALI, and the exosome co-expression network and ceRNA network related to ALI in sepsis.
Keywords: acute lung injury; ceRNA networks; inflammation; lung tissue exosomes; sepsis.
© 2023 Deng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Construction of a potentially functional lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in sepsis by bioinformatics analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 15;13:1031589. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1031589. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36457745 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and integrated analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs associated with periodontitis in humans.J Periodontal Res. 2021 Aug;56(4):679-689. doi: 10.1111/jre.12864. Epub 2021 Mar 9. J Periodontal Res. 2021. PMID: 33751610 Free PMC article.
-
Whole transcriptome analysis of the differential RNA profiles and associated competing endogenous RNA networks in LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI).PLoS One. 2021 May 7;16(5):e0251359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251359. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33961683 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Aberrantly Expressed Profiles of lncRNAs and miRNAs with Associated ceRNA Network in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Jul;26(3):1935-1945. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00780-4. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 31898160
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

