DNA Structure Design Is Improved Using an Artificially Expanded Alphabet of Base Pairs Including Loop and Mismatch Thermodynamic Parameters
- PMID: 37671922
- PMCID: PMC10510751
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00358
DNA Structure Design Is Improved Using an Artificially Expanded Alphabet of Base Pairs Including Loop and Mismatch Thermodynamic Parameters
Abstract
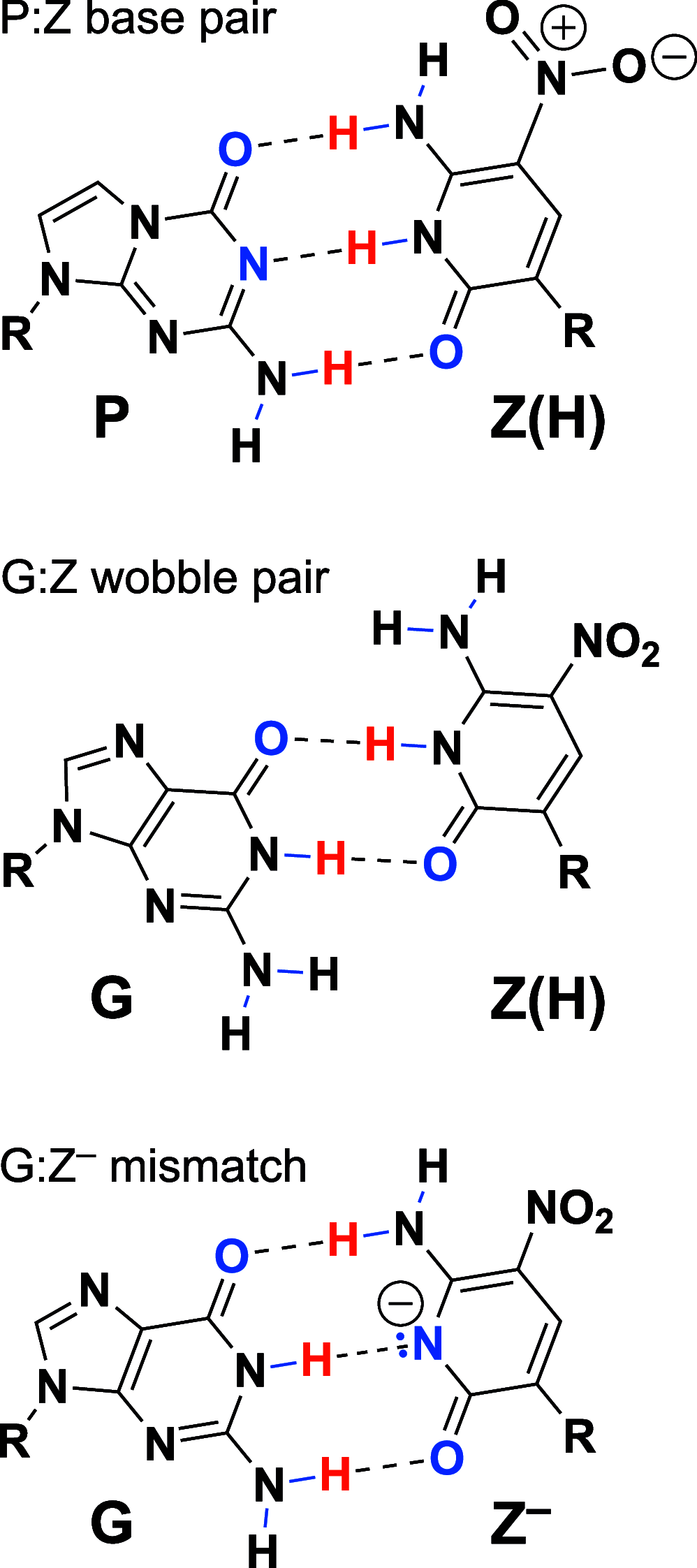
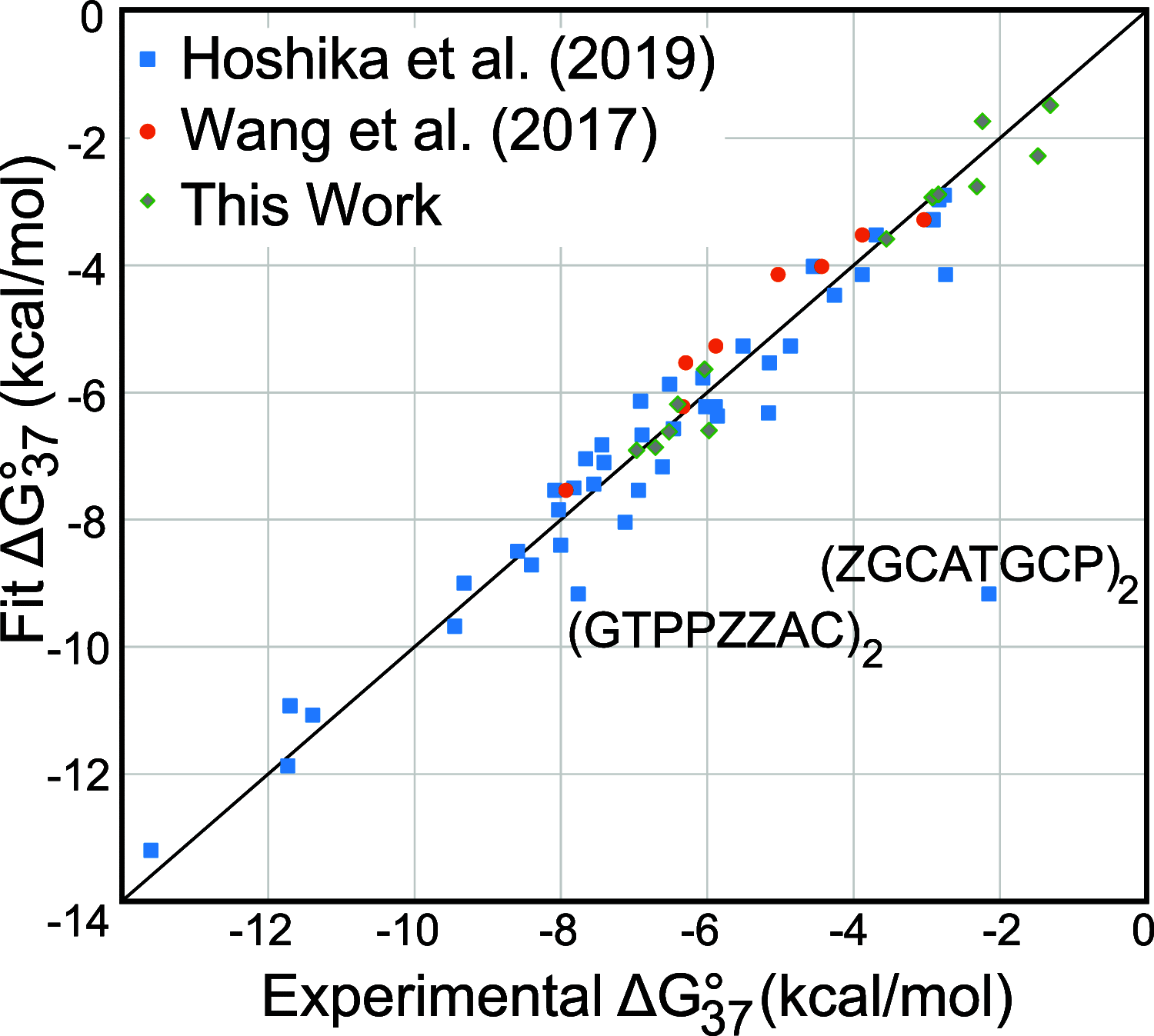
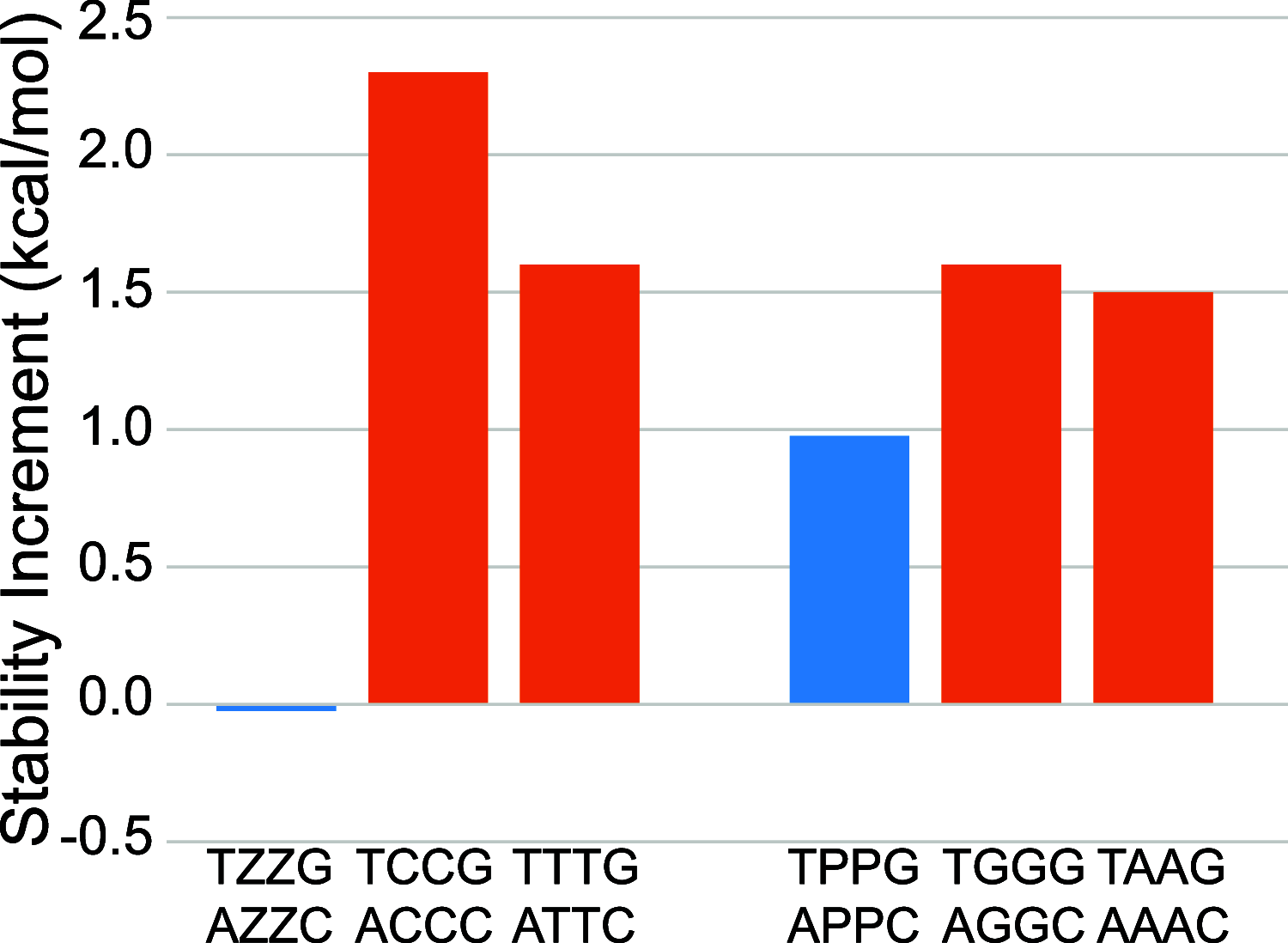
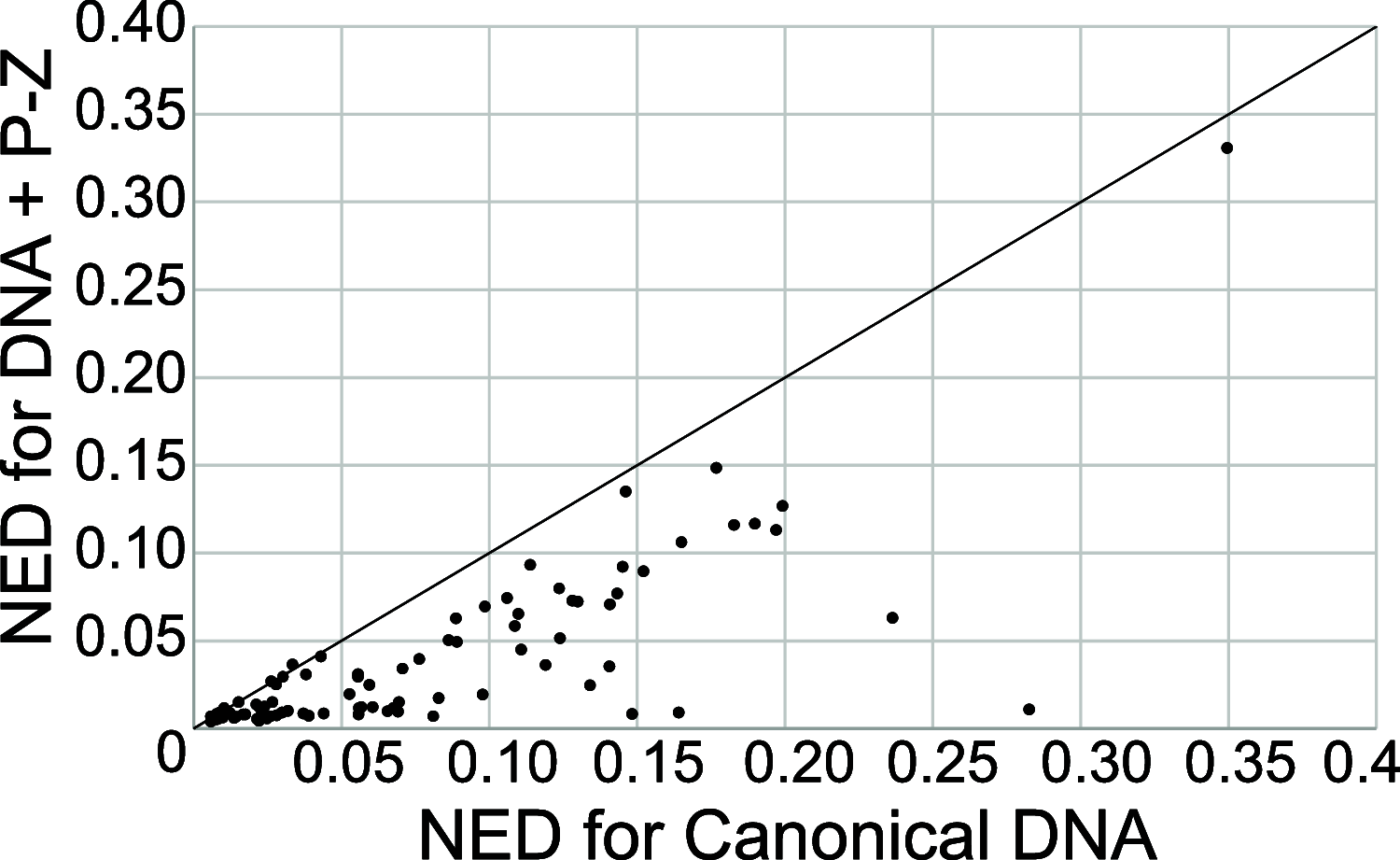
We show that in silico design of DNA secondary structures is improved by extending the base pairing alphabet beyond A-T and G-C to include the pair between 2-amino-8-(1'-β-d-2'-deoxyribofuranosyl)-imidazo-[1,2-a]-1,3,5-triazin-(8H)-4-one and 6-amino-3-(1'-β-d-2'-deoxyribofuranosyl)-5-nitro-(1H)-pyridin-2-one, abbreviated as P and Z. To obtain the thermodynamic parameters needed to include P-Z pairs in the designs, we performed 47 optical melting experiments and combined the results with previous work to fit free energy and enthalpy nearest neighbor folding parameters for P-Z pairs and G-Z wobble pairs. We find G-Z pairs have stability comparable to that of A-T pairs and should therefore be included as base pairs in structure prediction and design algorithms. Additionally, we extrapolated the set of loop, terminal mismatch, and dangling end parameters to include the P and Z nucleotides. These parameters were incorporated into the RNAstructure software package for secondary structure prediction and analysis. Using the RNAstructure Design program, we solved 99 of the 100 design problems posed by Eterna using the ACGT alphabet or supplementing it with P-Z pairs. Extending the alphabet reduced the propensity of sequences to fold into off-target structures, as evaluated by the normalized ensemble defect (NED). The NED values were improved relative to those from the Eterna example solutions in 91 of 99 cases in which Eterna-player solutions were provided. P-Z-containing designs had average NED values of 0.040, significantly below the 0.074 of standard-DNA-only designs, and inclusion of the P-Z pairs decreased the time needed to converge on a design. This work provides a sample pipeline for inclusion of any expanded alphabet nucleotides into prediction and design workflows.
Keywords: DNA folding thermodynamics; DNA secondary structure design; expanded DNA alphabet; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): DNA Analytics applied for a U.S. patent, PCT/US23/64288 (Generating Parameters to Predict Hybridization Strength of Nucleic Acid Sequences), to protect the applicable optical melt curve fit methods.
Figures

Update of
-
DNA Structure Design Is Improved Using an Artificially Expanded Alphabet of Base Pairs Including Loop and Mismatch Thermodynamic Parameters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 8:2023.06.06.543917. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.06.543917. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Sep 15;12(9):2750-2763. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00358 PMID: 37333404 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
DNA Structure Design Is Improved Using an Artificially Expanded Alphabet of Base Pairs Including Loop and Mismatch Thermodynamic Parameters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 8:2023.06.06.543917. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.06.543917. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Sep 15;12(9):2750-2763. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00358 PMID: 37333404 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Biophysics of Artificially Expanded Genetic Information Systems. Thermodynamics of DNA Duplexes Containing Matches and Mismatches Involving 2-Amino-3-nitropyridin-6-one (Z) and Imidazo[1,2-a]-1,3,5-triazin-4(8H)one (P).ACS Synth Biol. 2017 May 19;6(5):782-792. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00224. Epub 2017 Feb 9. ACS Synth Biol. 2017. PMID: 28094993
-
Recognition of an expanded genetic alphabet by type-II restriction endonucleases and their application to analyze polymerase fidelity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 May;39(9):3949-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1274. Epub 2011 Jan 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21245035 Free PMC article.
-
Toward an Expanded Genome: Structural and Computational Characterization of an Artificially Expanded Genetic Information System.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Jun 20;50(6):1375-1382. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00655. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28594167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic alphabet expansion biotechnology by creating unnatural base pairs.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2018 Jun;51:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29049900 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequence Design Using RNAstructure.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2847:17-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4079-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39312134
-
Datasets for Benchmarking RNA Design Algorithms.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2847:229-240. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4079-1_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39312148
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

