S100A6: molecular function and biomarker role
- PMID: 37670392
- PMCID: PMC10481514
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-023-00515-3
S100A6: molecular function and biomarker role
Abstract
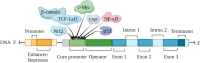
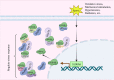
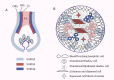
S100A6 (also called calcyclin) is a Ca2+-binding protein that belongs to the S100 protein family. S100A6 has many functions related to the cytoskeleton, cell stress, proliferation, and differentiation. S100A6 also has many interacting proteins that are distributed in the cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, and outside the cell. Almost all these proteins interact with S100A6 in a Ca2+-dependent manner, and some also have specific motifs responsible for binding to S100A6. The expression of S100A6 is regulated by several transcription factors (such as c-Myc, P53, NF-κB, USF, Nrf2, etc.). The expression level depends on the specific cell type and the transcription factors activated in specific physical and chemical environments, and is also related to histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and other epigenetic modifications. The differential expression of S100A6 in various diseases, and at different stages of those diseases, makes it a good biomarker for differential diagnosis and prognosis evaluation, as well as a potential therapeutic target. In this review, we mainly focus on the S100A6 ligand and its transcriptional regulation, molecular function (cytoskeleton, cell stress, cell differentiation), and role as a biomarker in human disease and stem cells.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cell differentiation; Cellular stress response; Cytoskeleton; S100A6; Stem cells; Tumor.
© 2023. Yumed Inc. and BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic control of the S100A6 (calcyclin) gene expression.J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Oct;127(10):2307-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700879. Epub 2007 May 10. J Invest Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17495951
-
The Role of S100A6 in Human Diseases: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 17;13(7):1139. doi: 10.3390/biom13071139. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium-regulated interaction of Sgt1 with S100A6 (calcyclin) and other S100 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 18;278(29):26923-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211518200. Epub 2003 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12746458
-
Involvement of NF-kappaB in the regulation of S100A6 gene expression in human hepatoblastoma cell line HepG2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Jul 25;307(2):274-80. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)01199-9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 12859951
-
S100A6 - focus on recent developments.Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 26;398(10):1087-1094. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2017-0125. Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28343163 Review.
Cited by
-
PARK7/DJ-1 deficiency impairs microglial activation in response to LPS-induced inflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Jul 16;21(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03164-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 39014482 Free PMC article.
-
ST8Sia2 polysialyltransferase protects against infection by Trypanosoma cruzi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Sep 25;18(9):e0012454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012454. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39321148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lesniak W, Filipek A. Ca2+-dependent interaction of calcyclin with membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;220(2):269–273. - PubMed
-
- Stradal TB, Gimona M. Ca(2+)-dependent association of S100A6 (Calcyclin) with the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(44):31593–31596. - PubMed
-
- Filipek A, Michowski W, Kuznicki J. Involvement of S100A6 (calcyclin) and its binding partners in intracellular signaling pathways. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2008;48:225–239. - PubMed
-
- Filipek A, Leśniak W. Current view on cellular function of S100A6 and its ligands, CacyBP/SIP and Sgt1. Postepy Biochem. 2018;64(3):242–252. - PubMed
-
- Sastry M, Ketchem RR, Crescenzi O, et al. The three-dimensional structure of Ca(2+)-bound calcyclin: implications for Ca(2+)-signal transduction by S100 proteins. Structure. 1998;6(2):223–231. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

