Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1 (ADAR1) as crucial regulators in cardiovascular diseases: structures, pathogenesis, and potential therapeutic approach
- PMID: 37663249
- PMCID: PMC10469703
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1194884
Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1 (ADAR1) as crucial regulators in cardiovascular diseases: structures, pathogenesis, and potential therapeutic approach
Abstract
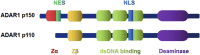
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a group of diseases that have a major impact on global health and are the leading cause of death. A large number of chemical base modifications in ribonucleic acid (RNA) are associated with cardiovascular diseases. A variety of ribonucleic acid modifications exist in cells, among which adenosine deaminase-dependent modification is one of the most common ribonucleic acid modifications. Adenosine deaminase acting on ribonucleic acid 1 (Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1) is a widely expressed double-stranded ribonucleic acid adenosine deaminase that forms inosine (A-to-I) by catalyzing the deamination of adenosine at specific sites of the target ribonucleic acid. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the structure of Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1 and summarize the regulatory mechanisms of ADAR1-mediated ribonucleic acid editing in cardiovascular diseases, indicating Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1 as a promising therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: ADAR1; RNA editing; cardiovascular diseases; potential therapeutic approach; target gene regulation.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Jin, Jiang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An RNA editor, adenosine deaminase acting on double-stranded RNA (ADAR1).J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014 Jun;34(6):437-46. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0001. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014. PMID: 24905200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA editing by ADAR1 leads to context-dependent transcriptome-wide changes in RNA secondary structure.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 13;8(1):1440. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01458-8. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29129909 Free PMC article.
-
RNA binding by ADAR3 inhibits adenosine-to-inosine editing and promotes expression of immune response protein MAVS.J Biol Chem. 2022 Sep;298(9):102267. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102267. Epub 2022 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35850307 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA 1 Associates with Orf Virus OV20.0 and Enhances Viral Replication.J Virol. 2019 Mar 21;93(7):e01912-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01912-18. Print 2019 Apr 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30651363 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR1 in stem cell fate and function.Biomark Res. 2023 Jun 6;11(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00503-7. Biomark Res. 2023. PMID: 37280687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing the hidden RBP-RNA interactions with RNA modification enzyme-based strategies.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 May-Jun;15(3):e1863. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1863. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 39392204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAR1 Is Essential for Smooth Muscle Homeostasis and Vascular Integrity.Cells. 2024 Jul 26;13(15):1257. doi: 10.3390/cells13151257. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120288 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

