The Correlation Between C-Peptide and Severity of Peripheral Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 37663202
- PMCID: PMC10474844
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S426956
The Correlation Between C-Peptide and Severity of Peripheral Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: One of the major issues affecting global health is Diabetes mellitus (DM), not only in terms of the disease itself but also its complications. Macrovascular complications are both common and serious, affecting many patients. This study aimed to assess fasting C-peptide levels and correlate them with the severity of the peripheral arterial disease complicating type 2 DM (T2DM).
Patients and methods: This study included 200 participants who were categorized into two groups: Group I (n=100, patients with T2DM complicated by femoropopliteal arterial atherosclerosis) and Group II (n=100, healthy age- and sex-matched individuals serving as controls). Fasting C-peptide levels were estimated using an immunochemiluminometric assay.
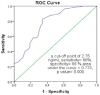
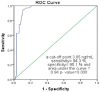
Results: Fasting C-peptide levels were significantly higher in Group I than in the control group. Fasting C-peptide levels were positively correlated with the severity of atherosclerosis. In addition, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis revealed that fasting C-peptide levels served as a specific and sensitive marker for detecting the severity of this disease.
Conclusion: Fasting C-peptide levels can be used as a sensitive and specific indicator of the severity of femoropopliteal arteriosclerosis that complicates T2DM.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; fasting C-peptide; femoropopliteal arteriosclerosis.
© 2023 Wahab et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary C-peptide creatinine ratio to differentiate type 2 diabetes mellitus from type 1 in pediatric patients.Eur J Pediatr. 2020 Jul;179(7):1115-1120. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03606-7. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Eur J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32052124 Clinical Trial.
-
The Association of Fasting C-peptide with Corneal Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Dec 2;2020:8883736. doi: 10.1155/2020/8883736. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 33344652 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between serum cystatin-C levels and vibrating perception threshold in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Jan;41(1):58-64. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2016.01.009. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 26819426 Chinese.
-
Remnant cholesterol is independently asssociated with an increased risk of peripheral artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 15;14:1111152. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1111152. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36875452 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-cell response to intravenous glucagon in African-American and Hispanic children with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jan;15(1):59-67. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2002.15.1.59. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 11822582 Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources