This is a preprint.
A suppressor screen in C. elegans identifies a multi-protein interaction interface that stabilizes the synaptonemal complex
- PMID: 37662357
- PMCID: PMC10473659
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.08.21.554166
A suppressor screen in C. elegans identifies a multi-protein interaction interface that stabilizes the synaptonemal complex
Update in
-
A suppressor screen in C. elegans identifies a multiprotein interaction that stabilizes the synaptonemal complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 12;120(50):e2314335120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2314335120. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38055743 Free PMC article.
Abstract
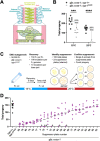
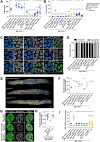
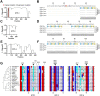
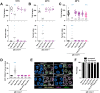
Successful chromosome segregation into gametes depends on tightly-regulated interactions between the parental chromosomes. During meiosis, chromosomes are aligned end-to-end by an interface called the synaptonemal complex, which also regulates exchanges between them. However, despite the functional and ultrastructural conservation of this essential interface, how protein-protein interactions within the synaptonemal complex regulate chromosomal interactions remains poorly understood. Here we describe a novel interaction interface in the C. elegans synaptonemal complex, comprised of short segments of three proteins, SYP-1, SYP-3 and SYP-4. We identified the interface through a saturated suppressor screen of a mutant that destabilizes the synaptonemal complex. The specificity and tight distribution of suppressors point to a charge-based interface that promotes interactions between synaptonemal complex subunits and, in turn, allows intimate interactions between chromosomes. Our work highlights the power of genetic studies to illuminate the mechanisms that underly meiotic chromosome interactions.
Keywords: BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES; C. elegans; Genetics; crossover; meiosis; suppressor screen; synaptonemal complex.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A suppressor screen in C. elegans identifies a multiprotein interaction that stabilizes the synaptonemal complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 12;120(50):e2314335120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2314335120. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38055743 Free PMC article.
-
A yeast two-hybrid screen for SYP-3 interactors identifies SYP-4, a component required for synaptonemal complex assembly and chiasma formation in Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000669. Epub 2009 Oct 2. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19798442 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptonemal Complex Central Region Proteins Promote Localization of Pro-crossover Factors to Recombination Events During Caenorhabditis elegans Meiosis.Genetics. 2019 Oct;213(2):395-409. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302625. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31431470 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and resolution of meiotic chromosome entanglements and interlocks.J Cell Sci. 2024 Jul 1;137(13):jcs262004. doi: 10.1242/jcs.262004. Epub 2024 Jul 10. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 38985540 Review.
-
Building the synaptonemal complex: Molecular interactions between the axis and the central region.PLoS Genet. 2023 Jul 20;19(7):e1010822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010822. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37471284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hassold T., Sherman S., Hunt P., Counting cross-overs: characterizing meiotic recombination in mammals. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 2409–2419 (2000). - PubMed
-
- van Veen J. E., Hawley R. S., Meiosis: when even two is a crowd. Curr. Biol. 13, R831–3 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Page S. L., Hawley R. S., The genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 525–558 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
