Effects of Dopamine on stem cells and its potential roles in the treatment of inflammatory disorders: a narrative review
- PMID: 37649087
- PMCID: PMC10469852
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03454-w
Effects of Dopamine on stem cells and its potential roles in the treatment of inflammatory disorders: a narrative review
Abstract
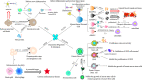
Inflammation is the host's protective response against harmful external stimulation that helps tissue repair and remodeling. However, excessive inflammation seriously threatens the patient's life. Due to anti-inflammatory effects, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and monoclonal antibodies are used to treat various inflammatory diseases, but drug resistance, non-responsiveness, and severe side effect limit their development and application. Therefore, developing other alternative therapies has become essential in anti-inflammatory therapy. In recent years, the in-depth study of stem cells has made them a promising alternative drug for the treatment of inflammatory diseases, and the function of stem cells is regulated by a variety of signals, of which dopamine signaling is one of the main influencing factors. In this review, we review the effects of dopamine on various adult stem cells (neural stem cells, mesenchymal stromal cells, hematopoietic stem cells, and cancer stem cells) and their signaling pathways, as well as the application of some critical dopamine receptor agonists/antagonists. Besides, we also review the role of various adult stem cells in inflammatory diseases and discuss the potential anti-inflammation function of dopamine receptors, which provides a new therapeutic target for regenerative medicine in inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Cancer stem cell; Dopamine; Hematopoietic stem cell; Inflammatory disorders; Mesenchymal stromal cell; Neuron stem cell.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Staphylococcus aureus on stem cells and potential targeted treatment of inflammatory disorders.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jun 27;15(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03781-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38937829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Function and Regulation of BMP6 in Various Kinds of Stem Cells.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(25):3634-43. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150710150218. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26166606 Review.
-
Redirecting adult mesenchymal stromal cells to the brain: a new approach for treating CNS autoimmunity and neuroinflammation?Immunol Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;96(4):347-357. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12014. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Immunol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29377354 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell suppresses the efficacy of CAR-T toward killing lymphoma cells by modulating the microenvironment through stanniocalcin-1.Elife. 2023 Feb 13;12:e82934. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82934. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36779699 Free PMC article.
-
Migratory strategies of normal and malignant stem cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;750:25-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-145-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21618081
Cited by
-
Dopaminergic Input Regulates the Sensitivity of Indirect Pathway Striatal Spiny Neurons to Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor.Biology (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;12(10):1360. doi: 10.3390/biology12101360. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warren N, O'Gorman C, Lehn A, Siskind D. Dopamine dysregulation syndrome in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review of published cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017;88(12):1060–1064. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg LI. Cardiovascular and renal actions of dopamine: potential clinical applications. Pharmacol Rev. 1972;24(1):1–29. - PubMed
-
- Murphy MB. Dopamine: a role in the pathogenesis and treatment of hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2000;14(Suppl 1):S47–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources