Pancreatic draining lymph nodes (PLNs) serve as a pathogenic hub contributing to the development of type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 37641145
- PMCID: PMC10464122
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-023-01110-7
Pancreatic draining lymph nodes (PLNs) serve as a pathogenic hub contributing to the development of type 1 diabetes
Abstract
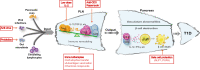
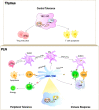
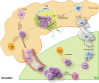
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a chronic, progressive autoinflammatory disorder resulting from the breakdown of self-tolerance and unrestrained β cell-reactive immune response. Activation of immune cells is initiated in islet and amplified in lymphoid tissues, especially those pancreatic draining lymph nodes (PLNs). The knowledge of PLNs as the hub of aberrant immune response is continuously being replenished and renewed. Here we provide a PLN-centered view of T1D pathogenesis and emphasize that PLNs integrate signal inputs from the pancreas, gut, viral infection or peripheral circulation, undergo immune remodeling within the local microenvironment and export effector cell components into pancreas to affect T1D progression. In accordance, we suggest that T1D intervention can be implemented by three major ways: cutting off the signal inputs into PLNs (reduce inflammatory β cell damage, enhance gut integrity and control pathogenic viral infections), modulating the immune activation status of PLNs and blocking the outputs of PLNs towards pancreatic islets. Given the dynamic and complex nature of T1D etiology, the corresponding intervention strategy is thus required to be comprehensive to ensure optimal therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: PLN remodeling; Pancreatic draining lymph nodes (PLNs); Signal inputs; Signal outputs; Type 1 diabetes (T1D).
© 2023. Society of Chinese Bioscientists in America (SCBA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gut microbiota translocation to the pancreatic lymph nodes triggers NOD2 activation and contributes to T1D onset.J Exp Med. 2016 Jun 27;213(7):1223-39. doi: 10.1084/jem.20150744. Epub 2016 Jun 20. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27325889 Free PMC article.
-
Th1-Like ICOS+ Foxp3+ Treg Cells Preferentially Express CXCR3 and Home to β-Islets during Pre-Diabetes in BDC2.5 NOD Mice.PLoS One. 2015 May 6;10(5):e0126311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126311. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25946021 Free PMC article.
-
Immune perturbations in human pancreas lymphatic tissues prior to and after type 1 diabetes onset.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 16:2024.04.23.590798. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.23.590798. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345402 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The interferon regulatory factors, a double-edged sword, in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.Cell Immunol. 2022 Sep;379:104590. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2022.104590. Epub 2022 Aug 13. Cell Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36030565 Review.
-
Lymphotoxins Serve as a Novel Orchestrator in T1D Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 9;13:917577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.917577. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35757751 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential contribution of gut microbiota in the development of autoantibodies in T1D children carrying HLA-DRB1/DQB1 risk alleles: an experimental and in silico analysis.Immunogenetics. 2024 Dec;76(5-6):335-349. doi: 10.1007/s00251-024-01354-8. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Immunogenetics. 2024. PMID: 39276210
-
N-Myc and STAT Interactor is an Endometriosis Suppressor.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8145. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158145. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gepts W. Islet changes suggesting a possible immune aetiology of human diabetes mellitus. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1976;205:95–106. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

