rRNA transcription is integral to phase separation and maintenance of nucleolar structure
- PMID: 37639467
- PMCID: PMC10513380
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010854
rRNA transcription is integral to phase separation and maintenance of nucleolar structure
Abstract
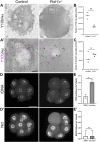
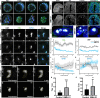
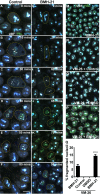
Transcription of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) by RNA Polymerase (Pol) I in the nucleolus is necessary for ribosome biogenesis, which is intimately tied to cell growth and proliferation. Perturbation of ribosome biogenesis results in tissue specific disorders termed ribosomopathies in association with alterations in nucleolar structure. However, how rRNA transcription and ribosome biogenesis regulate nucleolar structure during normal development and in the pathogenesis of disease remains poorly understood. Here we show that homozygous null mutations in Pol I subunits required for rRNA transcription and ribosome biogenesis lead to preimplantation lethality. Moreover, we discovered that Polr1a-/-, Polr1b-/-, Polr1c-/- and Polr1d-/- mutants exhibit defects in the structure of their nucleoli, as evidenced by a decrease in number of nucleolar precursor bodies and a concomitant increase in nucleolar volume, which results in a single condensed nucleolus. Pharmacological inhibition of Pol I in preimplantation and midgestation embryos, as well as in hiPSCs, similarly results in a single condensed nucleolus or fragmented nucleoli. We find that when Pol I function and rRNA transcription is inhibited, the viscosity of the granular compartment of the nucleolus increases, which disrupts its phase separation properties, leading to a single condensed nucleolus. However, if a cell progresses through mitosis, the absence of rRNA transcription prevents reassembly of the nucleolus and manifests as fragmented nucleoli. Taken together, our data suggests that Pol I function and rRNA transcription are required for maintaining nucleolar structure and integrity during development and in the pathogenesis of disease.
Copyright: © 2023 Dash et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleolar Pol II interactome reveals TBPL1, PAF1, and Pol I at intergenic rDNA drive rRNA biogenesis.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 6;15(1):9603. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54002-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39505901 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the UBF gene induces aberrant somatic nucleolar bodies and disrupts embryo nucleolar precursor bodies.Gene. 2017 May 15;612:5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.09.013. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Gene. 2017. PMID: 27614293
-
Distinct states of nucleolar stress induced by anticancer drugs.Elife. 2023 Dec 15;12:RP88799. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88799. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38099650 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond rRNA: nucleolar transcription generates a complex network of RNAs with multiple roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis.Genes Dev. 2022 Aug 1;36(15-16):876-886. doi: 10.1101/gad.349969.122. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 36207140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleolar stress: From development to cancer.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 28;136:64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.001. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35410715 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active RNA synthesis patterns nuclear condensates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 13:2024.10.12.614958. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.12.614958. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39498261 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Phase Separation as a Driver of Stem Cell Organization and Function during Development.J Dev Biol. 2023 Dec 12;11(4):45. doi: 10.3390/jdb11040045. J Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38132713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An RNA-centric view of transcription and genome organization.Mol Cell. 2024 Oct 3;84(19):3627-3643. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.08.021. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39366351 Review.
-
Nucleolar dynamics are determined by the ordered assembly of the ribosome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 15:2023.09.26.559432. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.26.559432. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 37808656 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Clustering of rRNA operons in E. coli is disrupted by σH.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 21:2024.09.20.614170. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.20.614170. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345417 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

