Assembling a Cinnamyl Pharmacophore in the C3-Position of Substituted Isatins via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Development of a New Class of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 37630420
- PMCID: PMC10458360
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28166167
Assembling a Cinnamyl Pharmacophore in the C3-Position of Substituted Isatins via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Development of a New Class of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
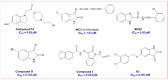
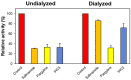
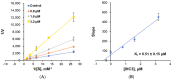
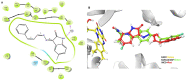
Monoamine oxidase (MAO, EC 1.4.3.4) is responsible for the oxidative breakdown of both endogenous and exogenous amines and exists in MAO-A and MAO-B isomers. Eighteen indole-based phenylallylidene derivatives were synthesized via nucleophilic addition reactions comprising three sub-series, IHC, IHMC, and IHNC, and were developed and examined for their ability to inhibit MAO. Among them, compound IHC3 showed a strong MAO-B inhibitory effect with an IC50 (half-maximal inhibitory concentration) value of 1.672 μM, followed by IHC2 (IC50 = 16.934 μM). Additionally, IHC3 showed the highest selectivity index (SI) value of >23.92. The effectiveness of IHC3 was lower than the reference pargyline (0.14 μM); however, the SI value was higher than pargyline (17.16). Structurally, the IHC (-H in the B-ring) sub-series exhibited relatively stronger MAO-B inhibition than the others. In the IHC series, IHC3 (-F in the A-ring) exhibited stronger MAO-B suppression than the other substituted derivatives in the order -F > -Br > -Cl > -OCH3, -CH3, and -H at the 2-position in the A-ring. In the reversibility and enzyme kinetics experiments, IHC3 was a reversible inhibitor with a Ki value of 0.51 ± 0.15 μM for MAO-B. Further, it was observed that IHC3 greatly decreased the cell death caused by rotenone in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. A molecular docking study of the lead molecule was also performed to determine hypothetical interactions in the enzyme-binding cavity. These findings suggest that IHC3 is a strong, specific, and reversible MAO-B inhibitor that can be used to treat neurological diseases.
Keywords: indole-based phenylallylidene derivatives; kinetics; molecular docking; monoamine oxidase inhibitors; neurological diseases; neuroprotection; reversibility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploration of a new class of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors by assembling benzyloxy pharmacophore on halogenated chalcones.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023 Aug;102(2):271-284. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14238. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023. PMID: 37011915
-
Halogenated class of oximes as a new class of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors for the treatment of Parkinson's disease: Synthesis, biochemistry, and molecular dynamics study.Comput Biol Chem. 2023 Aug;105:107899. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2023.107899. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Comput Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37315342
-
Isatin-tethered halogen-containing acylhydrazone derivatives as monoamine oxidase inhibitor with neuroprotective effect.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 13;14(1):1264. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51728-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38218887 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of monoamine oxidases and neuroprotective effects: chalcones vs. chromones.Mol Divers. 2024 Aug 15. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10959-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 39145880
-
Exploration of the Detailed Structure-Activity Relationships of Isatin and Their Isomers As Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors.ACS Omega. 2022 May 5;7(19):16244-16259. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01470. eCollection 2022 May 17. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35601305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multireceptor Analysis for Evaluating the Antidiabetic Efficacy of Karanjin: A Computational Approach.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024 Jul;7(4):e509. doi: 10.1002/edm2.509. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38982323 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and in vitro and in silico studies of morpholine derived thiazoles as bovine carbonic anhydrase-II inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 8;14(30):21355-21374. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03385j. eCollection 2024 Jul 5. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38979463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sonawane R.P., Tripathi R.R. The chemistry and synthesis of 1H-indole-2,3-dione (isatin) and its derivatives. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2013;7:30–36. doi: 10.56431/p-8lif75. - DOI
-
- Khan F.A., Maalik A. Advances in pharmacology of isatin and its derivatives: A review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2015;14:1937–1942. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v14i10.28. - DOI
-
- Grewal A.S. Isatin derivatives with several biological activities. J. Int. Pharm. Res. 2014;6:1–7.
-
- Da Silva J.F., Garden S.J., Pinto A.C. The chemistry of isatins: A review from 1975 to 1999. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2001;12:273–324. doi: 10.1590/S0103-50532001000300002. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

