Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations Interfere with Several Immune Components and Predict Poor Clinical Outcome
- PMID: 37626750
- PMCID: PMC10452213
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11082254
Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations Interfere with Several Immune Components and Predict Poor Clinical Outcome
Abstract
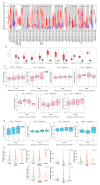
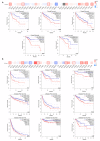
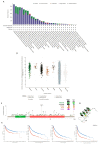
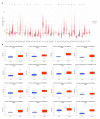
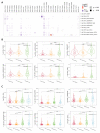
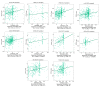
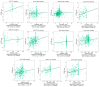
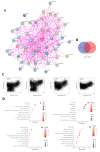
Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A) is a well-known tumor suppressor gene as it functions as a cell cycle regulator. While several reports correlate the malfunction of CDKN2A with the initiation and progression of several types of human tumors, there is a lack of a comprehensive study that analyzes the potential effect of CDKN2A genetic alterations on the human immune components and the consequences of that effect on tumor progression and patient survival in a pan-cancer model. The first stage of the current study was the analysis of CDKN2A differential expression in tumor tissues and the corresponding normal ones and correlating that with tumor stage, grade, metastasis, and clinical outcome. Next, a detailed profile of CDKN2A genetic alteration under tumor conditions was described and assessed for its effect on the status of different human immune components. CDKN2A was found to be upregulated in cancerous tissues versus normal ones and that predicted the progression of tumor stage, grade, and metastasis in addition to poor prognosis under different forms of tumors. Additionally, CDKN2A experienced different forms of genetic alteration under tumor conditions, a characteristic that influenced the infiltration and the status of CD8, the chemokine CCL4, and the chemokine receptor CCR6. Collectively, the current study demonstrates the potential employment of CDKN2A genetic alteration as a prognostic and immunological biomarker under several types of human cancers.
Keywords: CDKN2A; differential expression; epigenetic alteration; genetic alteration; immunotherapy; patient survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A Gene as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Colon Adenocarcinoma.Cureus. 2024 May 19;16(5):e60586. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60586. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38894777 Free PMC article.
-
The cell senescence regulator p16 is a promising cancer prognostic and immune check-point inhibitor (ICI) therapy biomarker.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Mar 23;15(6):2136-2157. doi: 10.18632/aging.204601. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36961395 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analyses of cuproptosis-related gene CDKN2A on prognosis and immunologic therapy in human tumors.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Apr 7;102(14):e33468. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033468. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37026918 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations of CDKN2A (p16(INK4a)) in Cancer.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jun;8:30-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.04.017. Epub 2016 May 3. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27428416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular control of the cell cycle in cancer: biological and clinical aspects.Dan Med Bull. 2003 May;50(2):118-38. Dan Med Bull. 2003. PMID: 12812137 Review.
References
-
- Soltan M.A., Eldeen M.A., Eid R.A., Alyamani N.M., Alqahtani L.S., Albogami S., Jafri I., Park M.N., Alsharif G., Fayad E., et al. A pan-cancer analysis reveals CHD1L as a prognostic and immunological biomarker in several human cancers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023;10:1017148. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1017148. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soltan M.A., Eldeen M.A., Sajer B.H., Abdelhameed R.F.A., Al-Salmi F.A., Fayad E., Jafri I., Ahmed H.E.M., Eid R.A., Hassan H.M., et al. Integration of Chemoinformatics and Multi-Omics Analysis Defines ECT2 as a Potential Target for Cancer Drug Therapy. Biology. 2023;12:613. doi: 10.3390/biology12040613. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

