The Association between Serum Adiponectin Levels and Endothelial Function in Non-Dialysis-Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
- PMID: 37626670
- PMCID: PMC10452815
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11082174
The Association between Serum Adiponectin Levels and Endothelial Function in Non-Dialysis-Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Abstract
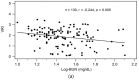
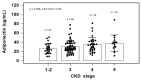
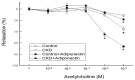
Adiponectin is the richest human circulating adipokine with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and insulin-sensitizing effects. We evaluated the association between serum adiponectin levels and endothelial function in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, obtaining fasting blood samples from 130 non-dialysis CKD subjects. We measured the endothelial function-represented by the vascular reactivity index (VRI)-via non-invasive digital thermal monitoring, and serum adiponectin concentrations by enzyme immunoassay kits. A total of 22 (16.9%), 39 (30.0%), and 69 (53.1%) patients had poor (VRI < 1.0), intermediate (1.0 ≤ VRI < 2.0), and good (VRI ≥ 2.0) vascular reactivity. Elevated serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level was negatively correlated with VRI values, but serum adiponectin and estimated glomerular filtration rate were positively associated with VRI values by univariate linear regression analysis. After applying multivariate stepwise linear regression analysis adjustment, the significantly positive association of adiponectin (p < 0.001), and the significantly negative association of log-BUN (p = 0.021) with VRI values in CKD subjects remained. In an animal study using in vitro blood-vessel myography, treatment with adiponectin enhancing acetylcholine-mediated vasorelaxation in 5/6 nephrectomy CKD mice. Our study results indicated that adiponectin concentration was positively associated with VRI values and modulated endothelial function in non-dialysis CKD patients.
Keywords: adiponectin; blood-vessel myography; chronic kidney disease; digital thermal monitoring test; endothelial function; vascular reactivity index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between Serum Indoxyl Sulfate Levels and Endothelial Function in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Oct 11;11(10):589. doi: 10.3390/toxins11100589. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31614554 Free PMC article.
-
Serum adiponectin level is positively associated with vascular reactivity index by digital thermal monitoring in patients with coronary artery disease.Tzu Chi Med J. 2023 Jun 1;35(4):348-354. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_30_23. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. Tzu Chi Med J. 2023. PMID: 38035059 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Galectin-3 Level Is Positively Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3 to 5.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jul 29;13(8):532. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080532. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437403 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin in chronic kidney disease has an opposite impact on protein-energy wasting and cardiovascular risk: two sides of the same coin.Clin Nephrol. 2009 Aug;72(2):87-96. doi: 10.5414/cnp72087. Clin Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19640365 Review.
-
Adiponectin and chronic kidney disease; a review on recent findings.J Nephropharmacol. 2015 Jul 27;4(2):63-68. eCollection 2015. J Nephropharmacol. 2015. PMID: 28197480 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level Is Positively Associated with Vascular Reactivity Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Nutrients. 2024 May 23;16(11):1575. doi: 10.3390/nu16111575. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892508 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

