Safety Concerns Related to the Simultaneous Use of Prescription or Over-the-Counter Medications and Herbal Medicinal Products: Survey Results among Latvian Citizens
- PMID: 37623137
- PMCID: PMC10454617
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20166551
Safety Concerns Related to the Simultaneous Use of Prescription or Over-the-Counter Medications and Herbal Medicinal Products: Survey Results among Latvian Citizens
Abstract
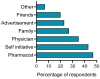
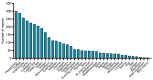
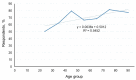
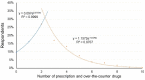
The use of herbal medicines is increasing worldwide. While the safety profile of many herbal medicines is promising, the data in the literature show important interactions with conventional drugs that can expose individual patients to high risk. The aim of this study was to investigate the experience of the use of herbal medicines and preparations and the risks of interactions between herbal and conventional medicines among Latvian citizens. Data were collected between 2019 and 2021 using a structured questionnaire designed for pharmacy customers in Latvia. Electronic databases such as Drugs.com, Medscape, and European Union herbal monographs were reviewed for the risk of drug interactions and potential side effects when herbal medicines were involved. The survey included 504 respondents. Of all the participants, 77.8% used herbal preparations. Most of the participants interviewed used herbal remedies based on the recommendation of the pharmacist or their own initiative. A total of 38.3% found the use of herbal remedies safe and harmless, while 57.3% of respondents regarded the combination of herbal and regular drugs as unsafe. The identified herbal medicines implicated in the potential risk of serious interactions were grapefruit, St. John's wort, and valerian. As the risks of herb-drug interactions were identified among the respondents, in the future, both pharmacy customers and healthcare specialists should pay more attention to possible herb-drug interactions of over-the-counter and prescription medications.
Keywords: adverse drug effects; consumer attitude; herbal medicines; herb–drug interactions; pharmacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consumers' attitude towards the use and safety of herbal medicines and herbal dietary supplements in Serbia.Int J Clin Pharm. 2013 Oct;35(5):835-40. doi: 10.1007/s11096-013-9819-3. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Int J Clin Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23820895
-
The emerging recognition of herb-drug interactions with a focus on St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum).Psychopharmacol Bull. 2001 Winter;35(1):53-64. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2001. PMID: 12397870 Review.
-
Medicinal plants and their preparations in the European market: Why has the harmonization failed? The cases of St. John's wort, valerian, ginkgo, ginseng, and green tea.Phytomedicine. 2021 Jan;81:153421. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153421. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33291029 Review.
-
[Potential risks, adverse effects and drug interactions associated with herbal medicine in dental patients].Refuat Hapeh Vehashinayim (1993). 2004 Apr;21(2):25-41, 97. Refuat Hapeh Vehashinayim (1993). 2004. PMID: 15503544 Review. Hebrew.
-
Potential interactions between herbal medicines and conventional drug therapies used by older adults attending a memory clinic.Drugs Aging. 2002;19(11):879-86. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200219110-00005. Drugs Aging. 2002. PMID: 12428996
Cited by
-
Interaction of Garcinia cambogia (Gaertn.) Desr. and Drugs as a Possible Mechanism of Liver Injury: The Case of Montelukast.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Sep 16;12(9):1771. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091771. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia-Alvarez A., Egan B., de Klein S., Dima L., Maggi F.M., Isoniemi M., Ribas-Barba L., Raats M.M., Meissner E.M., Badea M., et al. Usage of Plant Food Supplements across Six European Countries: Findings from the PlantLIBRA Consumer Survey. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e92265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092265. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

