An injectable conductive hydrogel with dual responsive release of rosmarinic acid improves cardiac function and promotes repair after myocardial infarction
- PMID: 37621769
- PMCID: PMC10444974
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.07.007
An injectable conductive hydrogel with dual responsive release of rosmarinic acid improves cardiac function and promotes repair after myocardial infarction
Abstract
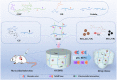
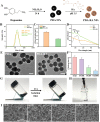
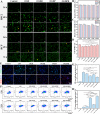
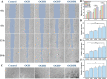
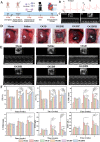
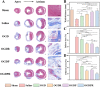
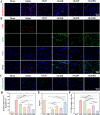
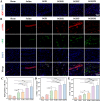
Myocardial infarction (MI) causes irreversible damage to the heart muscle, seriously threatening the lives of patients. Injectable hydrogels have attracted extensive attention in the treatment of MI. By promoting the coupling of mechanical and electrical signals between cardiomyocytes, combined with synergistic therapeutic strategies targeting the pathological processes of inflammation, proliferation, and fibrotic remodeling after MI, it is expected to improve the therapeutic effect. In this study, a pH/ROS dual-responsive injectable hydrogel was developed by modifying xanthan gum and gelatin with reversible imine bond and boronic ester bond double crosslinking. By encapsulating polydopamine-rosmarinic acid nanoparticles to achieve on-demand drug release in response to the microenvironment of MI, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-fibrosis effects. By adding conductive composites to improve the conductivity and mechanical strength of the hydrogel, restore electrical signal transmission in the infarct area, promote synchronous contraction of cardiomyocytes, avoid induced arrhythmias, and induce angiogenesis. Furthermore, the multifunctional hydrogel promoted the expression of cardiac-specific markers to restore cardiac function after MI. The in vivo and in vitro results demonstrate the effectiveness of this synergistic comprehensive treatment strategy in MI treatment, showing great application potential to promote the repair of infarcted hearts.
Keywords: Combined treatment; Conductivity; Myocardial infarction; Responsive hydrogel; Rosmarinic acid.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Zhiyong Qian is an editorial board member for Bioactive Materials and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An injectable conductive hydrogel restores electrical transmission at myocardial infarct site to preserve cardiac function and enhance repair.Bioact Mater. 2022 Jun 13;20:339-354. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.06.001. eCollection 2023 Feb. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 35784639 Free PMC article.
-
An injectable silk sericin hydrogel promotes cardiac functional recovery after ischemic myocardial infarction.Acta Biomater. 2016 Sep 1;41:210-23. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.05.039. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27262742
-
Injectable OPF/graphene oxide hydrogels provide mechanical support and enhance cell electrical signaling after implantation into myocardial infarct.Theranostics. 2018 May 12;8(12):3317-3330. doi: 10.7150/thno.25504. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29930732 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterial-Based Electrically Conductive Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Repair.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Dec 9;17:6181-6200. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S386763. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36531116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Advances of Injectable Functional Hydrogel Materials in the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction.Gels. 2022 Jul 6;8(7):423. doi: 10.3390/gels8070423. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35877508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanoparticles in Chitosan Hydrogels Enable Myocardial Infarction Repair through ROS Scavenging and Inhibition of Apoptosis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Nov 13;16(45):61551-61564. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c08155. Epub 2024 Sep 30. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39347611
-
Advanced Nanomedicine Approaches for Myocardial Infarction Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 24;19:6399-6425. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S467219. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38952676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing homogeneous networking principles for the development of fatigue-resistant, low-swelling and sprayable hydrogels for sealing wet, dynamic and concealed wounds in vivo.Bioact Mater. 2023 Dec 22;34:150-163. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.12.002. eCollection 2024 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 38225944 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Approach for Cardioprotection: In Situ Targeting of Metformin via Conductive Hydrogel System.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;16(15):2226. doi: 10.3390/polym16152226. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125251 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable Nano-Micro Composites with Anti-bacterial and Osteogenic Capabilities for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Osteomyelitis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Mar;11(12):e2306964. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306964. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38234236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vos T., Lim S.S., Abbafati C., Abbas K.M., Abbasi M., Abbasifard M., Abbasi-Kangevari M., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdelalim A. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories. 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019, The Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204–1222. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou M., Wang H., Zeng X., Yin P., Zhu J., Chen W., Li X., Wang L., Wang L., Liu Y., Liu J., Zhang M., Qi J., Yu S., Afshin A., Gakidou E., Glenn S., Krish V.S., Miller-Petrie M.K., Mountjoy-Venning W.C., Mullany E.C., Redford S.B., Liu H., Naghavi M., Hay S.I., Wang L., Murray C.J.L., Liang X. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394(10204):1145–1158. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiao L., Li M., Shao Y., Zhang Y., Gong M., Yang X., Wang Y., Tan Z., Sun L., Xuan L., Yu Q., Li Y., Gao Y., Liu H., Xu H., Li X., Zhang Y., Zhang Y. LncRNA-ZFAS1 induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by causing cytosolic Ca2+ overload in myocardial infarction mice model. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(12):942. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sutton M.G.S.J., Sharpe N. Left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2000;101(25):2981–2988. - PubMed
-
- Taimeh Z., Loughran J., Birks E.J., Bolli R. Vascular endothelial growth factor in heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013;10(9):519–530. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

