Exploring the potential of approved drugs for triple-negative breast cancer treatment by targeting casein kinase 2: Insights from computational studies
- PMID: 37578958
- PMCID: PMC10424868
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289887
Exploring the potential of approved drugs for triple-negative breast cancer treatment by targeting casein kinase 2: Insights from computational studies
Abstract
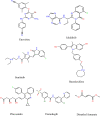
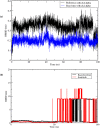
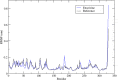
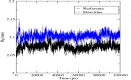
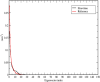
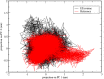
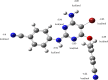
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive malignancy that requires effective targeted drug therapy. In this study, we employed in silico methods to evaluate the efficacy of seven approved drugs against human ck2 alpha kinase, a significant modulator of TNBC metastasis and invasiveness. Molecular docking revealed that the co-crystallized reference inhibitor 108600 achieved a docking score of (-7.390 kcal/mol). Notably, among the seven approved drugs tested, sunitinib, bazedoxifene, and etravirine exhibited superior docking scores compared to the reference inhibitor. Specifically, their respective docking scores were -10.401, -7.937, and -7.743 kcal/mol. Further analysis using MM/GBSA demonstrated that these three top-ranked drugs possessed better binding energies than the reference ligand. Subsequent molecular dynamics simulations identified etravirine, an FDA-approved antiviral drug, as the only repurposed drug that demonstrated a stable and reliable binding mode with the human ck2 alpha protein, based on various analysis measures including RMSD, RMSF, and radius of gyration. Principal component analysis indicated that etravirine exhibited comparable stability of motion as a complex with human ck2 alpha protein, similar to the co-crystallized inhibitor. Additionally, Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed on a complex of etravirine and a representative gold atom positioned at different sites relative to the heteroatoms of etravirine. The results of the DFT calculations revealed low-energy complexes that could potentially serve as guides for experimental trials involving gold nanocarriers of etravirine, enhancing its delivery to malignant cells and introducing a new drug delivery route. Based on the results obtained in this research study, etravirine shows promise as a potential antitumor agent targeting TNBC, warranting further investigation through experimental and clinical assessments.
Copyright: © 2023 Shoaib et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A drug design strategy based on molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations applied to development of inhibitor against triple-negative breast cancer by Scutellarein derivatives.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 12;18(10):e0283271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283271. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37824496 Free PMC article.
-
Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Revealed the Potential Inhibitory Activity of Amygdalin in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapeutics Targeting the BRCT Domain of BARD1 Receptor.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr;66(4):718-736. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00680-8. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 36732462
-
Identification of Genes Hub Associated with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Cannabidiol Analogs Potential Inhibitory Agents: An In-silico Study.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 May 1;25(5):1649-1661. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.5.1649. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38809637 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing Drugs as Novel Triple-negative Breast Cancer Therapeutics.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(3):515-550. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666211021143255. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34674627 Review.
-
Kinase inhibitors for precision therapy of triple-negative breast cancer: Progress, challenges, and new perspectives on targeting this heterogeneous disease.Cancer Lett. 2022 Oct 28;547:215775. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215775. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35667515 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the potential of phytochemicals to inhibit nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 2 for cancer: Pharmacophore screening, molecular docking, ADME properties, and molecular dynamics simulation investigations.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 20;19(8):e0308913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308913. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39163297 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Studies Reveal the Anticancer Potential of Medicinal-Plant-Derived Lignans as MDM2-P53 Interaction Inhibitors.Molecules. 2023 Sep 16;28(18):6665. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186665. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764441 Free PMC article.
-
Marine-Derived Compounds for CDK5 Inhibition in Cancer: Integrating Multi-Stage Virtual Screening, MM/GBSA Analysis and Molecular Dynamics Investigations.Metabolites. 2023 Oct 18;13(10):1090. doi: 10.3390/metabo13101090. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37887415 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

