Health Economic Analysis of Antiviral Drugs in the Global Polio Eradication Endgame
- PMID: 37577803
- PMCID: PMC10680042
- DOI: 10.1177/0272989X231191127
Health Economic Analysis of Antiviral Drugs in the Global Polio Eradication Endgame
Abstract
Background: Polio antiviral drugs (PAVDs) may provide a critical tool in the eradication endgame by stopping poliovirus infections in immunodeficient individuals who may not clear the virus without therapeutic intervention. Although prolonged/chronic poliovirus excreters are rare, they represent a source of poliovirus reintroduction into the general population. Prior studies that assumed the successful cessation of all oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) use estimated the potential upper bound of the incremental net benefits (INBs) of resource investments in research and development of PAVDs. However, delays in polio eradication, OPV cessation, and the development of PAVDs necessitate an updated economic analysis to reevaluate the costs and benefits of further investments in PAVDs.
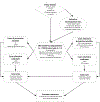
Methods: Using a global integrated model of polio transmission, immunity, vaccine dynamics, risks, and economics, we explore the risks of reintroduction of polio transmission due to immunodeficiency-related vaccine-derived poliovirus (iVDPV) excreters and reevaluate the upper bound of the INBs of PAVDs.
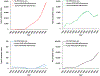
Results: Under the current conditions, for which the use of OPV will likely continue for the foreseeable future, even with successful eradication of type 1 wild poliovirus by the end of 2023 and continued use of Sabin OPV for outbreak response, we estimate an upper bound INB of 60 million US$2019. With >100 million US$2019 already invested in PAVD development and with the introduction of novel OPVs that are less likely to revert to neurovirulence, our analysis suggests the expected INBs of PAVDs would not offset their costs.
Conclusions: While PAVDs could play an important role in the polio endgame, their expected economic benefits drop with ongoing OPV use and poliovirus transmissions. However, stakeholders may pursue the development of PAVDs as a desired product regardless of their economic benefits.HighlightsWhile polio antiviral drugs could play an important role in the polio endgame, their expected economic benefits continue to drop with delays in polio eradication and the continued use of oral poliovirus vaccines.The incremental net benefits of investments in polio antiviral drug development and screening for immunodeficiency-related circulating polioviruses are small.Limited global resources are better spent on increasing global population immunity to polioviruses to stop and prevent poliovirus transmission.
Keywords: antiviral drugs; disease eradication; modeling; polio; prevention; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coordinated global cessation of oral poliovirus vaccine use: Options and potential consequences.Risk Anal. 2024 Feb;44(2):366-378. doi: 10.1111/risa.14158. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Risk Anal. 2024. PMID: 37344934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Complexity of options related to restarting oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) in national immunization programs after OPV cessation.Gates Open Res. 2023 Apr 17;7:55. doi: 10.12688/gatesopenres.14511.1. eCollection 2023. Gates Open Res. 2023. PMID: 37547300 Free PMC article.
-
Genedrive kit for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism m.1555A>G in neonates and their mothers: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(75):1-75. doi: 10.3310/TGAC4201. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487741 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Review of Poliovirus Transmission and Economic Modeling to Support Global Polio Eradication: 2020-2024.Pathogens. 2024 May 22;13(6):435. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13060435. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38921733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging perspectives on RNA virus-mediated infections: from pathogenesis to therapeutic interventions.World J Virol. 2023 Dec 25;12(5):242-255. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v12.i5.242. World J Virol. 2023. PMID: 38187500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increasing Population Immunity Prior to Globally-Coordinated Cessation of Bivalent Oral Poliovirus Vaccine (bOPV).Pathogens. 2024 Sep 17;13(9):804. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090804. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39338995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Polio post-certification strategy: A risk mitigation strategy for a polio-free world, https://polioeradication.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/polio-post-certi... (2018, accessed June 22 2022).
-
- MacCallum PO. Observations on the feeding of attenuated live polioviruses (Sabin) to children with hypogammaglobulinemia. Presented at the 9th Symposium of the European Association of Poliomyelitis and Allied Diseases. Stockholm, Sweden1963.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

