Challenges in Pharmacological Intervention in Perilipins (PLINs) to Modulate Lipid Droplet Dynamics in Obesity and Cancer
- PMID: 37568828
- PMCID: PMC10417315
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15154013
Challenges in Pharmacological Intervention in Perilipins (PLINs) to Modulate Lipid Droplet Dynamics in Obesity and Cancer
Abstract
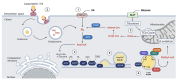
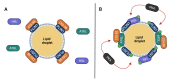
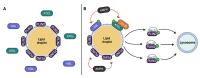
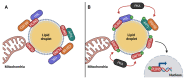
Perilipins (PLINs) are the most abundant proteins in lipid droplets (LD). These LD-associated proteins are responsible for upgrading LD from inert lipid storage structures to fully functional organelles, fundamentally integrated in the lipid metabolism. There are five distinct perilipins (PLIN1-5), each with specific expression patterns and metabolic activation, but all capable of regulating the activity of lipases on LD. This plurality creates a complex orchestrated mechanism that is directly related to the healthy balance between lipogenesis and lipolysis. Given the essential role of PLINs in the modulation of the lipid metabolism, these proteins can become interesting targets for the treatment of lipid-associated diseases. Since reprogrammed lipid metabolism is a recognized cancer hallmark, and obesity is a known risk factor for cancer and other comorbidities, the modulation of PLINs could either improve existing treatments or create new opportunities for the treatment of these diseases. Even though PLINs have not been, so far, directly considered for pharmacological interventions, there are many established drugs that can modulate PLINs activity. Therefore, the aim of this study is to assess the involvement of PLINs in diseases related to lipid metabolism dysregulation and whether PLINs can be viewed as potential therapeutic targets for cancer and obesity.
Keywords: cancer; lipid droplets; obesity; perilipins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Perilipins in Oxidative Stress-Implications for Cardiovascular Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;13(2):209. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020209. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of perilipin protein function in lipid droplet metabolism.FEBS Lett. 2024 May;598(10):1170-1198. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14792. Epub 2024 Jan 1. FEBS Lett. 2024. PMID: 38140813 Review.
-
Biogenesis and Breakdown of Lipid Droplets in Pathological Conditions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 7;9:826248. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.826248. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35198567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of oleosin and perilipins in yeast promotes formation of lipid droplets from the endoplasmic reticulum.J Cell Sci. 2013 Nov 15;126(Pt 22):5198-209. doi: 10.1242/jcs.131896. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 24006263
-
Opposite and redundant roles of the two Drosophila perilipins in lipid mobilization.J Cell Sci. 2012 Aug 1;125(Pt 15):3568-77. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101329. Epub 2012 Apr 14. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22505614
Cited by
-
Clinically Effective Molecules of Natural Origin for Obesity Prevention or Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 25;25(5):2671. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052671. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased skeletal muscle intramyocellular lipid droplet-mitochondrial contact contributes to myosteatosis in cancer cachexia.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):C684-C697. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00345.2024. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39010842
-
Lipid droplets in pathogen infection and host immunity.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Mar;45(3):449-464. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01189-1. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37993536 Review.
-
Exploring the impact of lipid droplets on the evolution and progress of hepatocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 16;12:1404006. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1404006. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38818407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

