Outside-in signaling through the major histocompatibility complex class-I cytoplasmic tail modulates glutamate receptor expression in neurons
- PMID: 37567897
- PMCID: PMC10421907
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38663-z
Outside-in signaling through the major histocompatibility complex class-I cytoplasmic tail modulates glutamate receptor expression in neurons
Abstract
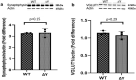
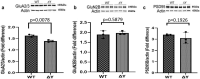
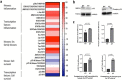
The interplay between AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) and major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) proteins in regulating synaptic signaling is a crucial aspect of central nervous system (CNS) function. In this study, we investigate the significance of the cytoplasmic tail of MHC-I in synaptic signaling within the CNS and its impact on the modulation of synaptic glutamate receptor expression. Specifically, we focus on the Y321 to F substitution (Y321F) within the conserved cytoplasmic tyrosine YXXΦ motif, known for its dual role in endocytosis and cellular signaling of MHC-I. Our findings reveal that the Y321F substitution influences the expression of AMPAR subunits GluA2/3 and leads to alterations in the phosphorylation of key kinases, including Fyn, Lyn, p38, ERK1/2, JNK1/2/3, and p70 S6 kinase. These data illuminate the crucial role of MHC-I in AMPAR function and present a novel mechanism by which MHC-I integrates extracellular cues to modulate synaptic plasticity in neurons, which ultimately underpins learning and memory.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The intracellular domain of major histocompatibility class-I proteins is essential for maintaining excitatory spine density and synaptic ultrastructure in the brain.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 20;13(1):6448. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30054-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37081001 Free PMC article.
-
GRIP1 regulates synaptic plasticity and learning and memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 6;117(40):25085-25091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014827117. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32948689 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
Acute knockdown of AMPA receptors reveals a trans-synaptic signal for presynaptic maturation.EMBO J. 2011 Apr 20;30(8):1577-92. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.59. Epub 2011 Mar 4. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21378752 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Roles and Evolutionary Significance of AMPA-Type Glutamate Receptors.Bioessays. 2018 Sep;40(9):e1800028. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800028. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 30058076 Review.
References
-
- Corriveau RA, Huh GS, Shatz CJ. Regulation of class I MHC gene expression in the developing and mature CNS by neural activity. Neuron. 1998;21(3):505–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

