New insights into the mechanochemical coupling mechanism of kinesin-microtubule complexes from their high-resolution structures
- PMID: 37560910
- PMCID: PMC10586761
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20221238
New insights into the mechanochemical coupling mechanism of kinesin-microtubule complexes from their high-resolution structures
Abstract
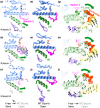
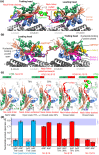
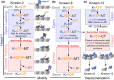
Kinesin motor proteins couple mechanical movements in their motor domain to the binding and hydrolysis of ATP in their nucleotide-binding pocket. Forces produced through this 'mechanochemical' coupling are typically used to mobilize kinesin-mediated transport of cargos along microtubules or microtubule cytoskeleton remodeling. This review discusses the recent high-resolution structures (<4 Å) of kinesins bound to microtubules or tubulin complexes that have resolved outstanding questions about the basis of mechanochemical coupling, and how family-specific modifications of the motor domain can enable its use for motility and/or microtubule depolymerization.
Keywords: cryo-electron microscopy; crystallography; kinesin; microtubule; molecular motors; tubulin.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
New Insights into the Coupling between Microtubule Depolymerization and ATP Hydrolysis by Kinesin-13 Protein Kif2C.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 24;290(30):18721-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646919. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26055718 Free PMC article.
-
The kinesin-5 tail domain directly modulates the mechanochemical cycle of the motor domain for anti-parallel microtubule sliding.Elife. 2020 Jan 20;9:e51131. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51131. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31958056 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM reveals the structural basis of microtubule depolymerization by kinesin-13s.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 25;9(1):1662. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04044-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29695795 Free PMC article.
-
These motors were made for walking.Protein Sci. 2020 Aug;29(8):1707-1723. doi: 10.1002/pro.3895. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Protein Sci. 2020. PMID: 32472639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinesin, 30 years later: Recent insights from structural studies.Protein Sci. 2015 Jul;24(7):1047-56. doi: 10.1002/pro.2697. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25975756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM unveils kinesin KIF1A's processivity mechanism and the impact of its pathogenic variant P305L.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 2;15(1):5530. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48720-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38956021 Free PMC article.
-
Tubulin CFEOM mutations both inhibit or activate kinesin motor activity.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Mar 1;35(3):ar32. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-01-0020. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38170592 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and regulation of kinesin motors.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Feb;26(2):86-103. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00780-6. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39394463 Review.
References
-
- Verhey, K.J., Cochran, J.C. and Walczak, C.E. (2015) The Kinesin Superfamily. In Kinesins and Cancer (Kozielski, F.S.B.F., ed.), pp. 1–26, Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

