HDAC6 inhibition: a significant potential regulator and therapeutic option to translate into clinical practice in renal transplantation
- PMID: 37545520
- PMCID: PMC10401441
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1168848
HDAC6 inhibition: a significant potential regulator and therapeutic option to translate into clinical practice in renal transplantation
Abstract
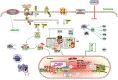
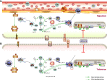
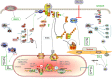
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6), an almost exclusively cytoplasmic enzyme, plays an essential role in many biological processes and exerts its deacetylation-dependent/independent effects on a variety of target molecules, which has contributed to the flourishing growth of relatively isoform-specific enzyme inhibitors. Renal transplantation (RT) is one of the alternatively preferred treatments and the most cost-effective treatment approaches for the great majority of patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). HDAC6 expression and activity have recently been shown to be increased in kidney disease in a number of studies. To date, a substantial amount of validated studies has identified HDAC6 as a pivotal modulator of innate and adaptive immunity, and HDAC6 inhibitors (HDAC6i) are being developed and investigated for use in arrays of immune-related diseases, making HDAC6i a promising therapeutic candidate for the management of a variety of renal diseases. Based on accumulating evidence, HDAC6i markedly open up new avenues for therapeutic intervention to protect against oxidative stress-induced damage, tip the balance in favor of the generation of tolerance-related immune cells, and attenuate fibrosis by inhibiting multiple activations of cell profibrotic signaling pathways. Taken together, we have a point of view that targeting HDAC6 may be a novel approach for the therapeutic strategy of RT-related complications, including consequences of ischemia-reperfusion injury, induction of immune tolerance in transplantation, equilibrium of rejection, and improvement of chronic renal graft interstitial fibrosis after transplantation in patients. Herein, we will elaborate on the unique function of HDAC6, which focuses on therapeutical mechanism of action related to immunological events with a general account of the tantalizing potential to the clinic.
Keywords: HDAC6; ameliorate outcomes; epigenetics; immunoregulation; molecular regulation; renal transplantation; selective HDAC6 inhibitors.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Zhang and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of HDAC6 activity in kidney diseases: a new perspective.Mol Med. 2018 Jun 26;24(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0027-4. Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30134806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase 6 inhibition mitigates renal fibrosis by suppressing TGF-β and EGFR signaling pathways in obstructive nephropathy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):F1003-F1014. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00261.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33103445 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of histone deacetylase 6 protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Clin Sci (Lond). 2018 Feb 2;132(3):339-359. doi: 10.1042/CS20171417. Print 2018 Feb 14. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29358506
-
Chasing a Breath of Fresh Air in Cystic Fibrosis (CF): Therapeutic Potential of Selective HDAC6 Inhibitors to Tackle Multiple Pathways in CF Pathophysiology.J Med Chem. 2022 Feb 24;65(4):3080-3097. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c02067. Epub 2022 Feb 11. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35148101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic hope for HDAC6 inhibitors in malignancy and chronic disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2016 Jun 1;130(12):987-1003. doi: 10.1042/CS20160084. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27154743 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc-Dependent Histone Deacetylases in Lung Endothelial Pathobiology.Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 23;14(2):140. doi: 10.3390/biom14020140. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in Alzheimer's disease: Mechanisms, clinical trials and new drug development strategies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Aug 23;9(1):211. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01911-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39174535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Histone Modifications in Kidney Fibrosis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 28;60(6):888. doi: 10.3390/medicina60060888. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38929505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Histone Deacetylase 6 and Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibition in Colorectal Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 29;16(1):54. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010054. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38258065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of human FOXP3+ Tregs: from homeostasis maintenance to pathogen defense.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 31;15:1444533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444533. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39144146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wouk N. End-stage renal disease: medical management. Am Fam Phys (2021) 104(5):493–9. - PubMed
-
- Erpicum P, Bonvoisin C, Grosch S, Bovy C, Pinto Coelho P, Detry O, et al. . Diagnostic et prise en charge thérapeutique du rejeten transplantation rénale [Diagnosis and management of renal allograft rejection]. Rev Med Liege (2022) 77(5-6):338–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

