Cooperative activation of PDK1 and AKT by MAPK4 enhances cancer growth and resistance to therapy
- PMID: 37531320
- PMCID: PMC10395914
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002227
Cooperative activation of PDK1 and AKT by MAPK4 enhances cancer growth and resistance to therapy
Abstract
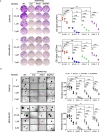
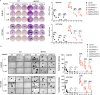
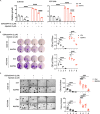
Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1) is a master kinase of the protein A, G, and C (AGC) family kinases that play important roles in regulating cancer cell proliferation, survival, and metabolism. Besides phosphorylating/activating AKT at the cell membrane in a PI3K-dependent manner, PDK1 also exhibits constitutive activity on many other AGC kinases for tumor-promoting activity. In the latter case, PDK1 protein levels dominate its activity. We previously reported that MAPK4, an atypical MAPK, can PI3K-independently promote AKT activation and tumor growth. Here, using triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell models, we demonstrate that MAPK4 can also enhance PDK1 protein synthesis, thus phosphorylate/activate PDK1 substrates beyond AKT. This new MAPK4-PDK1 axis alone lacks vigorous tumor-promoting activity but cooperates with our previously reported MAPK4-AKT axis to promote tumor growth. Besides enhancing resistance to PI3K blockade, MAPK4 also promotes cancer cell resistance to the more stringent PI3K and PDK1 co-blockade, a recently proposed therapeutic strategy. Currently, there is no MAPK4 inhibitor to treat MAPK4-high cancers. Based on the concerted action of MAPK4-AKT and MAPK4-PDK1 axis in promoting cancer, we predict and confirm that co-targeting AKT and PDK1 effectively represses MAPK4-induced cancer cell growth, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy to treat MAPK4-high cancers.
Copyright: © 2023 Han et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: FY is the co-founder and CEO of 4therapeutics Inc. He also holds an equity stake there. The other authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MAPK4 promotes triple negative breast cancer growth and reduces tumor sensitivity to PI3K blockade.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 11;13(1):245. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27921-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35017531 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated PDK1 Expression Drives PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Promotes Radiation-Resistant and Dedifferentiated Phenotype of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2020 Mar 18;9(3):746. doi: 10.3390/cells9030746. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32197467 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK4 overexpression promotes tumor progression via noncanonical activation of AKT/mTOR signaling.J Clin Invest. 2019 Mar 1;129(3):1015-1029. doi: 10.1172/JCI97712. Epub 2019 Jan 28. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30688659 Free PMC article.
-
PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Apr;15(2):161-70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.12.022. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15209375 Review.
-
PI3K signaling in cancer: beyond AKT.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;45:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28343126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Casamayor A, Morrice NA, Alessi DR. Phosphorylation of Ser-241 is essential for the activity of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1: identification of five sites of phosphorylation in vivo. Biochem J. 1999;342(Pt 2):287–92. Epub 1999/08/24. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1220463. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

