Genetic Structure and TALome Analysis Highlight a High Level of Diversity in Burkinabe Xanthomonas Oryzae pv. oryzae Populations
- PMID: 37523017
- PMCID: PMC10390441
- DOI: 10.1186/s12284-023-00648-x
Genetic Structure and TALome Analysis Highlight a High Level of Diversity in Burkinabe Xanthomonas Oryzae pv. oryzae Populations
Abstract
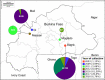
Bacterial Leaf Blight of rice (BLB) caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) is a major threat for food security in many rice growing countries including Burkina Faso, where the disease was first reported in the 1980's. In line with the intensification of rice cultivation in West-Africa, BLB incidence has been rising for the last 15 years. West-African strains of Xoo differ from their Asian counterparts as they (i) are genetically distant, (ii) belong to new races and, (iii) contain reduced repertoires of Transcription Activator Like (TAL) effector genes. In order to investigate the evolutionary dynamics of Xoo populations in Burkina Faso, 177 strains were collected from 2003 to 2018 in three regions where BLB is occurring. Multilocus VNTR Analysis (MLVA-14) targeting 10 polymorphic loci discriminated 24 haplotypes and showed that Xoo populations were structured according to their geographical localization and year of collection. Considering their major role in Xoo pathogenicity, we assessed the TAL effector repertoires of the 177 strains upon RFLP-based profiling. Surprisingly, an important diversity was revealed with up to eight different RFLP patterns. Finally, comparing neutral vs. tal effector gene diversity allowed to suggest scenarios underlying the evolutionary dynamics of Xoo populations in Burkina Faso, which is key to rationally guide the deployment of durably resistant rice varieties against BLB in the country.
Keywords: Bacterial leaf blight; Genotyping; Microsatellites; Molecular epidemiology; Rice; TALE; Xoo.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional and Genome Sequence-Driven Characterization of tal Effector Gene Repertoires Reveals Novel Variants With Altered Specificities in Closely Related Malian Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains.Front Microbiol. 2018 Aug 6;9:1657. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01657. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30127769 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of African Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae TALomes reveals a new susceptibility gene in bacterial leaf blight of rice.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jun 4;14(6):e1007092. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007092. eCollection 2018 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29864161 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Strains Isolated From Low Land and High Mountain Paddies in Guangxi, China.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 28;13:867633. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.867633. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35572630 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review.Rice (N Y). 2020 Jan 8;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 31915945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Rice Resistance to Bacterial Leaf Blight via Phytohormones.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;13(18):2541. doi: 10.3390/plants13182541. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in the Study of Natural Antimicrobial Active Substances in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Molecules. 2024 Sep 16;29(18):4400. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184400. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adhikari TB, Mew T, Teng P. Phenotypic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae in Nepal. Plant Dis. 1994;78:68–72. doi: 10.1094/PD-78-0068. - DOI
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA (1988) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

