The magnitude of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus, prediabetes, and associated factors among adults living in Debre Tabor town, northcentral Ethiopia: A community-based cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37519754
- PMCID: PMC10372355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17729
The magnitude of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus, prediabetes, and associated factors among adults living in Debre Tabor town, northcentral Ethiopia: A community-based cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a worldwide public health problem. The burden of diabetes has been continuously increasing from day to day, especially in developing countries like Ethiopia. Globally, half of all cases of diabetes mellitus are undiagnosed. Diabetes mellitus can be easily handled if it is detected early. There is limited evidence on the magnitude of undiagnosed diabetics and prediabetes at the community level in Ethiopia, particularly in the study area.
Objective: To assess the magnitude of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus, prediabetes, and associated factors among adults living in Debre Tabor town.
Methods: A community-based cross-sectional study was conducted in Debre Tabor town from October to December 2021. A total of 407 participants were selected using a multistage sampling technique. A pretested structural questionnaire was used to collect demographic, behavioral, and clinical data. Anthropometric measurements were taken with standardized and calibrated equipment. A fasting venous blood sample was collected for blood glucose level determination. Logistic regression was used to identify risk factors. A P-value ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
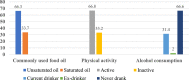
Result: The magnitude of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and prediabetes was found to be 4.5% (95% CI: 2.9-7.4) and 14.5% (95% CI: 11.1-18.1), respectively. Older age (AOR: 6.50, 95% CI: 1.82-23.21), abnormal body mass index (AOR: 6.84, 95% CI: 1.91-24.54), systolic hypertension (AOR: 8.74, 95% CI: 2.53-30.19), and family history of diabetes mellitus (FHDM) (AOR: 12.45, 95% CI: 3.63-42.65) were significantly associated with undiagnosed diabetes mellitus. Using saturated oil (AOR: 1.97, 95% CI: 1.09-3.55), having a high waist circumference (AOR: 2.16, 95% CI: 1.20-3.87), and being hypertensive (AOR: 2.26, 95% CI: 1.04-4.96) were all significantly associated with Prediabetes.
Conclusion: Adults in Debre Tabor town have a high prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes and prediabetes. A variety of modifiable risk factors were also identified. As a result, focusing the prevention strategy on such modifiable risk factors may help to minimize the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and prediabetes as well as future disease complications.
Keywords: Associated factors; Magnitude; Northcentral Ethiopia; Prediabetes; Undiagnosed diabetes mellitus.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus, Prediabetes and Its Associated Factors in Dessie Town, Northeast Ethiopia: A Community-Based Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Dec 31;12:2799-2809. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S225854. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 32021343 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of impaired fasting glucose and undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and associated risk factors among adults living in a rural Koladiba town, northwest Ethiopia.BMC Res Notes. 2017 Jul 6;10(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2571-3. BMC Res Notes. 2017. PMID: 28683811 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and associated factors among adult residents of Mizan Aman town, Southwest Ethiopia: Community-based cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2024 May 7;19(5):e0302167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302167. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38713690 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Primary Tooth Extraction and Its Associated Factors Among Under-Five-Year-Old Children in Debre Tabor Town, North-Central Ethiopia: Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Mar 2;16:837-846. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S383048. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 36910566 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular risk assessment in prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes mellitus study: international collaboration research overview.N Am J Med Sci. 2013 Nov;5(11):625-30. doi: 10.4103/1947-2714.122303. N Am J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24404539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetes mellitus service preparedness and availability: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 19;15:1427175. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1427175. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39099669 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10: A Key Antioxidant in the Management of Diabetes-Induced Cardiovascular Complications-An Overview of Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence.Int J Endocrinol. 2024 Mar 15;2024:2247748. doi: 10.1155/2024/2247748. eCollection 2024. Int J Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38524871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Undiagnosed hypertension and diabetes mellitus in the Tabari cohort: a population-based study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Nov 18;24(1):3199. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20701-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39558296 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking the silent epidemic: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of undiagnosed diabetes in Ethiopian adults.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 17;15:1372046. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1372046. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39086906 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and its associated factors in urban Burkina Faso.J Public Health Afr. 2024 Sep 16;15(1):497. doi: 10.4102/jphia.v15i1.497. eCollection 2024. J Public Health Afr. 2024. PMID: 39364302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2019. Classification of Diabetes Mellitus.
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; 2014. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials